
Lines of Symmetry for Regular Polygons Definition, Properties, Examples
A regular skew hexagon seen as edges (black) of a triangular antiprism, symmetry D 3d, [2 +,6], (2*3), order 12. A skew hexagon is a skew polygon with six vertices and edges but not existing on the same plane. The interior of such a hexagon is not generally defined. A skew zig-zag hexagon has vertices alternating between two parallel planes.
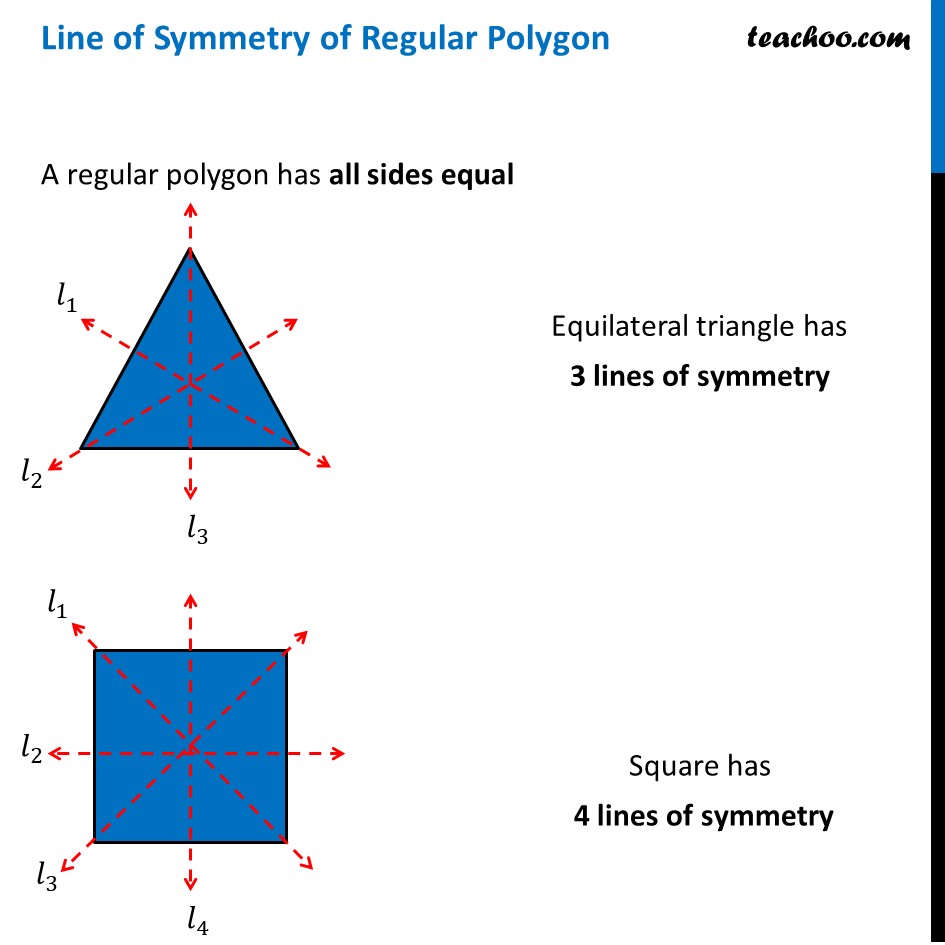
Line of Symmetry of Regular Polygon [with Formula and Examples]
Example 3: using angles. Show that the hexagon below has no lines of symmetry. Locate the centre of the 2D shape. Show step. Draw a small x x in the centre of the hexagon (this does not have to be exact): Use a ruler to visualise a horizontal and/or vertical line of symmetry through the centre of the shape.
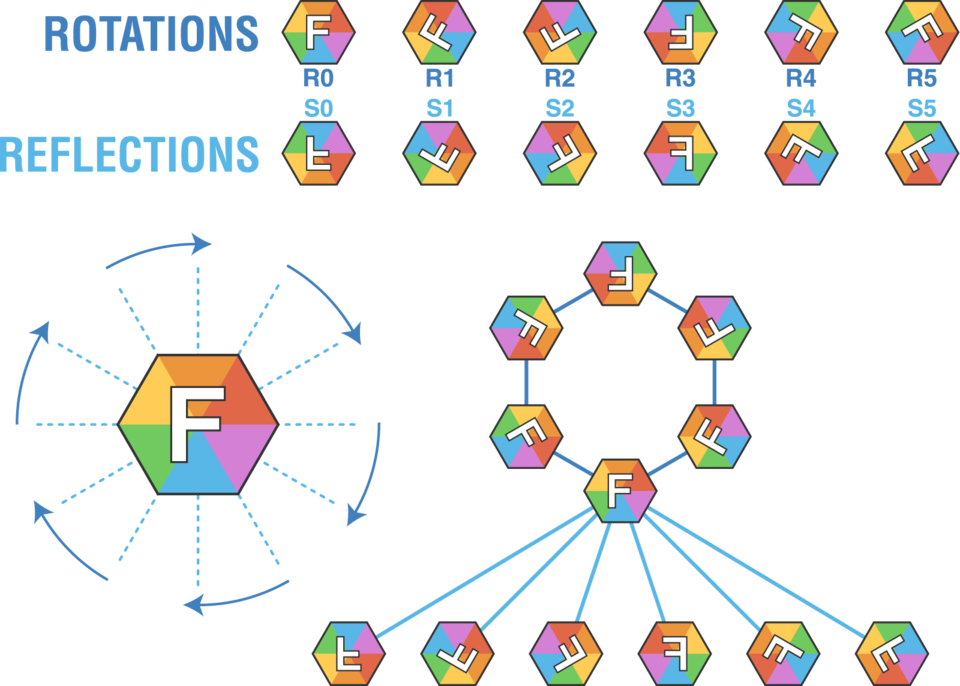
Symmetry group of a regular hexagon
4 Draw a line from each vertex through the center and check for line symmetry. 5 State the number of lines of symmetry. The equilateral triangle has 3 3 lines of symmetry. An equilateral triangle has 3 3 equal sides and 3 3 equal angles, so it will have 3 3 lines of symmetry.
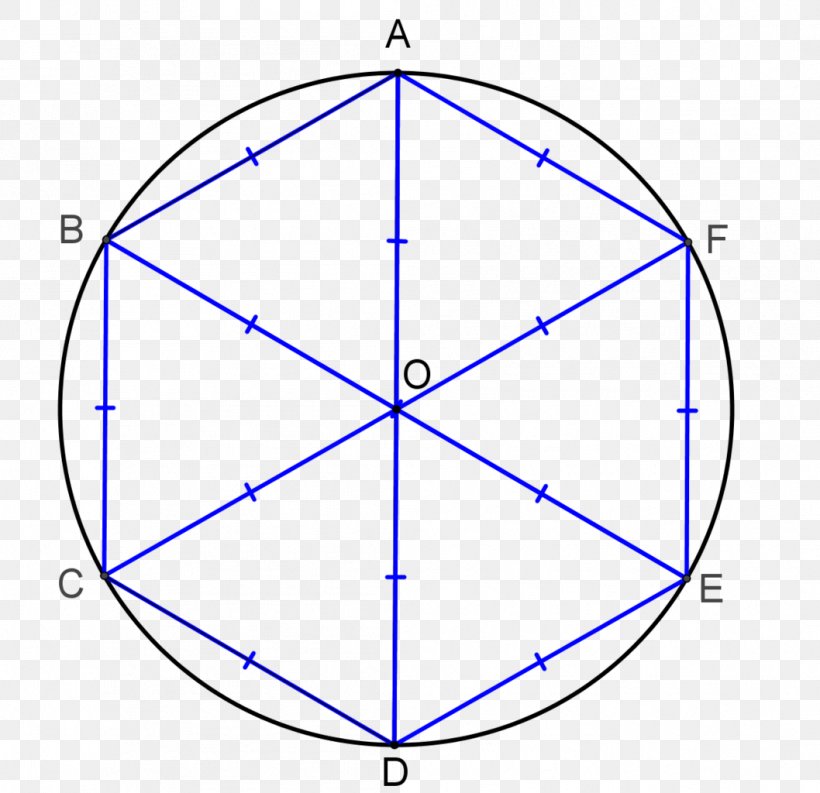
Hexagon Symmetry Triangle Regular Polygon Circle, PNG, 1058x1024px, Hexagon, Area, Axial
Draw the line of symmetry. 9. Draw a triangle that does not have a line of symmetry. Shade one more square so this pattern has one line of symmetry. 11. Here are some patterns. Circle any pattern that has a line of symmetry. 12. The diagram below shows a regular pentagon.

The diagram of the hexagon below displays all the lines of symmetry for the hexagon. True or
In a regular hexagon, if you know the value of the perimeter, you can calculate the length of each side by dividing the perimeter by six. For example, The regular hexagon shape below has a perimeter of 108 \, cm. 108 cm. You can calculate the length of each side by, 108 \div 6=18. 108 ÷ 6 = 18.
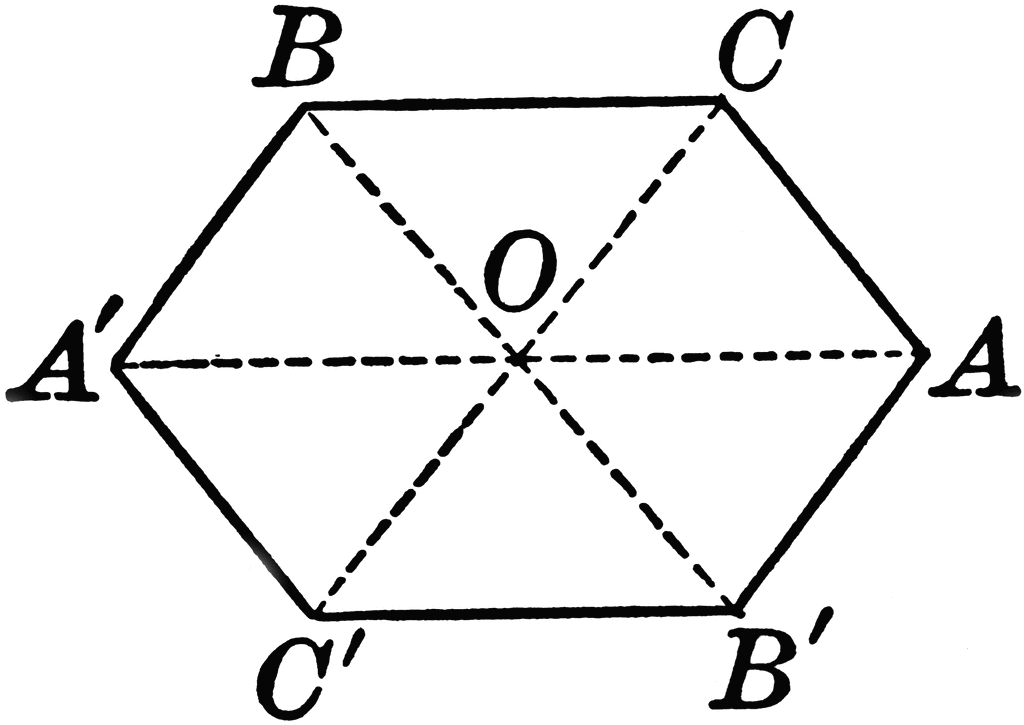
Axis of Symmetry Drawn on a Hexagon ClipArt ETC
A regular hexagon is defined as a closed 2D shape made up of six equal sides and six equal angles. Each angle of the regular hexagon measures 120°. The sum of all the interior angles is 120 × 6 = 720°. When it comes to the exterior angles, we know that the sum of exterior angles of any polygon is always 360°. There are 6 exterior angles in a hexagon.
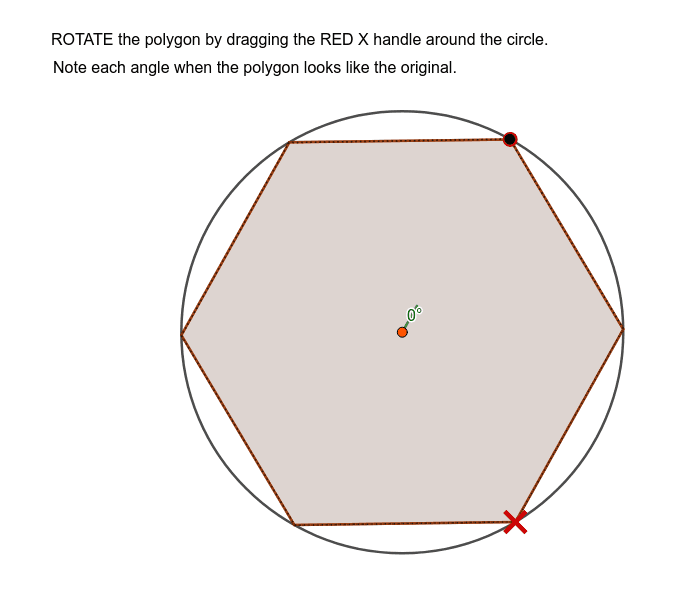
Hexagon Rotational Symmetry GeoGebra
Hexagon. Hexagons are 2D geometric polygons, known for being in honeycombs and pencils. A hexagon has six sides and six interior angles. Read on to find out more about the properties of these 6-sided shapes, including hexagon lines of symmetry. Download FREE teacher-made resources covering 'Hexagon'.
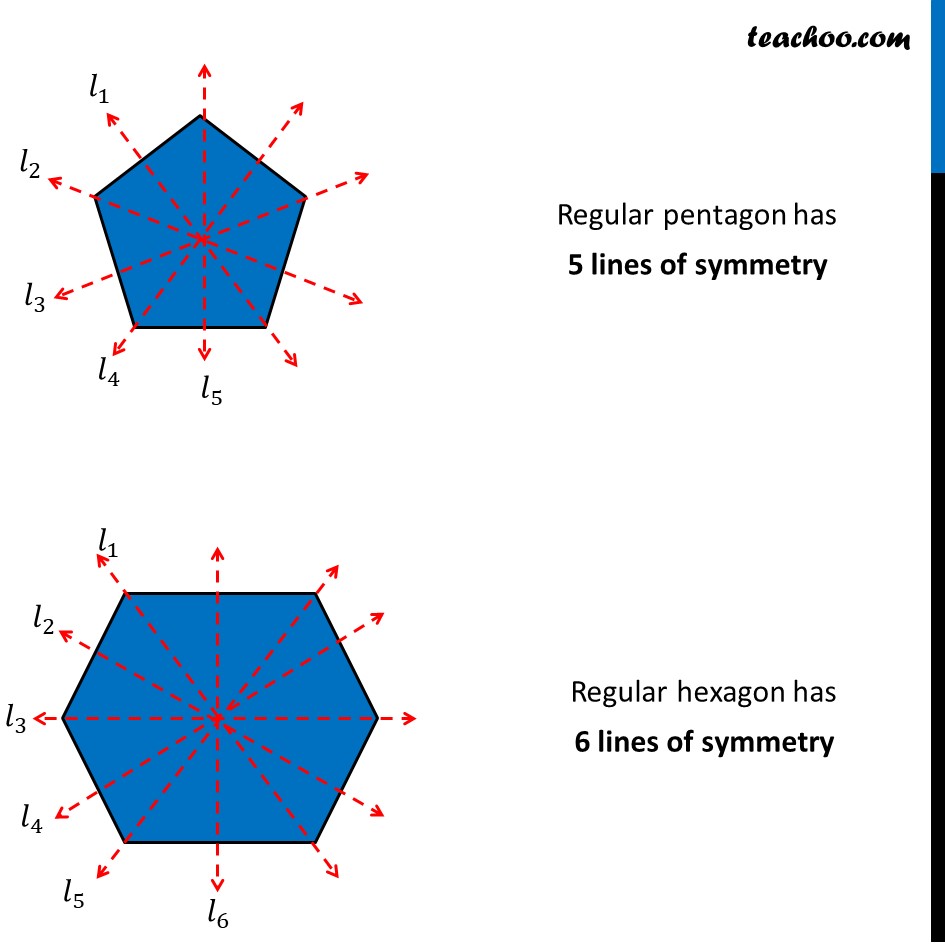
Line of Symmetry of Regular Polygon [with Formula and Examples]
A figure has line symmetry if it can be reflected across a line back onto itself. An isosceles triangle has one line of symmetry from its vertex to the midpoint of the base.. Rotating the regular hexagon 60° about its center maps the hexagon back onto itself. A space figure, such as a wheel, has rotational symmetry if the shape of the.

Lines of Symmetry Maths with Mum
A regular hexagon is a polygon with 6 sides of equal measure. Answer: A regular hexagon has 6 lines of symmetry. For all regular polygons, the number of lines of symmetry is equal to the number of sides. Explanation: Let's observe the following figure to understand the lines of symmetry of a regular hexagon. We can see that a regular hexagon.

Where Are The Lines Of Symmetry On A Hexagon? Mastery Wiki
Line of symmetry. A line of symmetry is a line that divides a figure into two identical parts. The figure below shows 3 line of symmetry examples.. Point A on the hexagon reflects to A' which is not on the hexagon. A line of symmetry is known as a rigid motion (or transformation) in geometry since the figure that is reflected across it does.
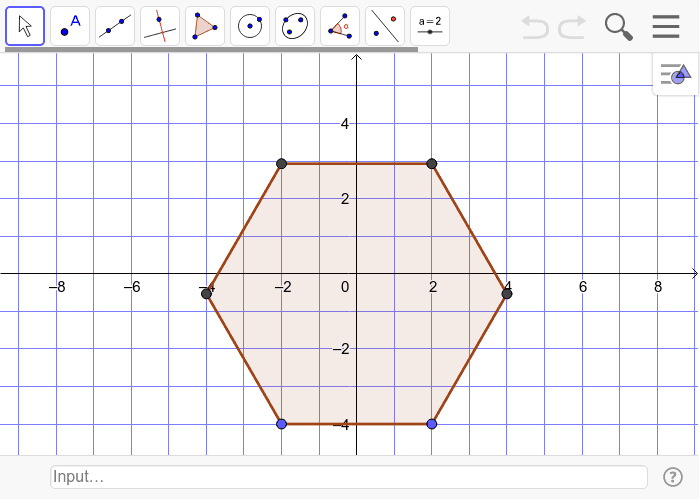
Regular Hexagon GeoGebra
Solution. Verified by Toppr. A regular hexagon with six equal sides has six lines of symmetry. For all regular polygons, the number of lines of symmetry is equal to the number of sides. That is an equilateral triangle has 3 lines of symmetry, a square has 4 lines of symmetry, similarly a regular hexagon has 6 lines of symmetry. The answer is 6.

Question 5e On a squared paper, sketch the hexagon with six lines of symmetry.
Symmetry examples. Lots of shapes have lines of symmetry, but some shapes have more than others. For example, a square has four lines of symmetry (one horizontal, one vertical, and two diagonal). On the other hand, some shapes have no lines of symmetry. For example, a circle and oval both have no lines of symmetry, because they're symmetrical.
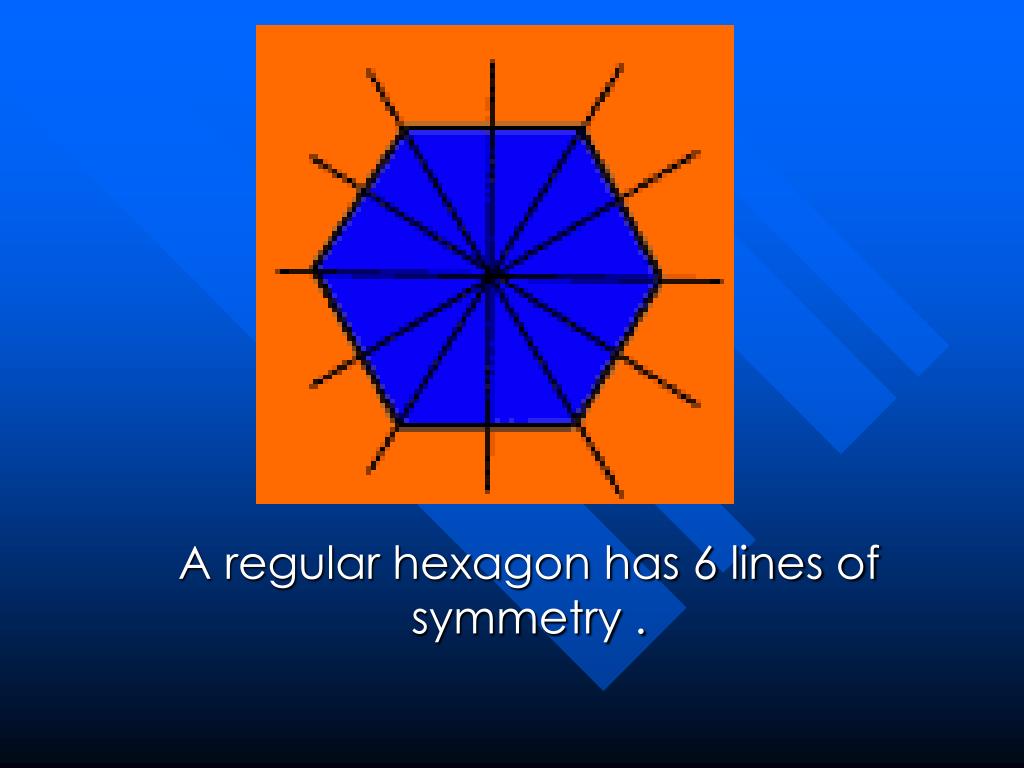
PPT Symmetry A Visual Presentation PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1454677
An Equilateral Triangle (3 sides) has 3 Lines of Symmetry. A Square (4 sides) has 4 Lines of Symmetry. A Regular Pentagon (5 sides) has 5 Lines of Symmetry. A Regular Hexagon (6 sides) has 6 Lines of Symmetry. A Regular Heptagon (7 sides)

Class 6 A hexagon with exactly two lines of symmetry Teachoo
A regular hexagon has 6 lines of symmetry and a rotational symmetry of order 6. 6 lines of symmetry: Six 60° angles of rotation: 2. Irregular Hexagon. In an irregular hexagon, the length of sides and measure of angles do not have the same measure. Related Worksheets. View.

Class 6 A hexagon with exactly two lines of symmetry Teachoo
The number of lines of symmetry for a shape can be determined by using a ruler to visualize when the shape or object can be divided equally into 2 equal pieces that are a reflection. the regular hexagon has 4 additional lines of symmetry. State the number of lines of symmetry. A regular hexagon has 6 lines of symmetry. Example 5: an.

Axes of Symmetry Hexagon KayleeaddBird
A line of symmetry is a line that you can draw across a shape and divide it into two mirror-images. That is to say, each half of the shape is the same, but looks like its been flipped from the other. You can also think of a line of symmetry as a line that you can draw, that when you fold the shape over the line both edges would line up exactly.
