
Symmetry Definition, Types, Examples (2022)
What is Point Symmetry? Point symmetry is when, given a central point on a shape or object, every point on the opposite sides is the same distance from the central point. Other terms for point.
Line and Point Symmetry YouTube
Point Symmetry: In geometry, there are different aspects associated with symmetry, and students need to understand the concept of symmetry. This concept is used by artists, professionals, clothes and jewellery designers, automobile manufacturers, architects, and others for different tasks associated with their respective professions.
Point Symmetry Prekinder to Grade 2 Mathematics
Rotational symmetry: When an object is rotated in a particular direction, around a point, then it is known as rotational symmetry. Reflexive symmetry: Reflective symmetry, also called mirror symmetry, is a type of symmetry where one half of the object reflects the other half of the object.

Symmetry Definition Solved Examples Geometry Cuemath
The conditions that a shape or a figure satisfies for point symmetry i.e. every part should have a matching part • the distance should be equal from the central point • but should be in the opposite direction. Related Concepts Linear Symmetry Lines of Symmetry Rotational Symmetry Order of Rotational Symmetry Types of Symmetry

Rotational Symmetry Definition, Properties, Angle of Symmetry, Examples
From other geometry videos and lessons we have learned about similarity and congruency in polygons, particularly triangles. In these lessons we intuitively learned that the position of the polygons did not matter when it comes to proving similarity and congruency. I.e. if two triangles are rotated 90 degrees from each other but have 2 sides and.

PPT 3.1 Symmetry & Coordinate Graphs PowerPoint Presentation ID2505676
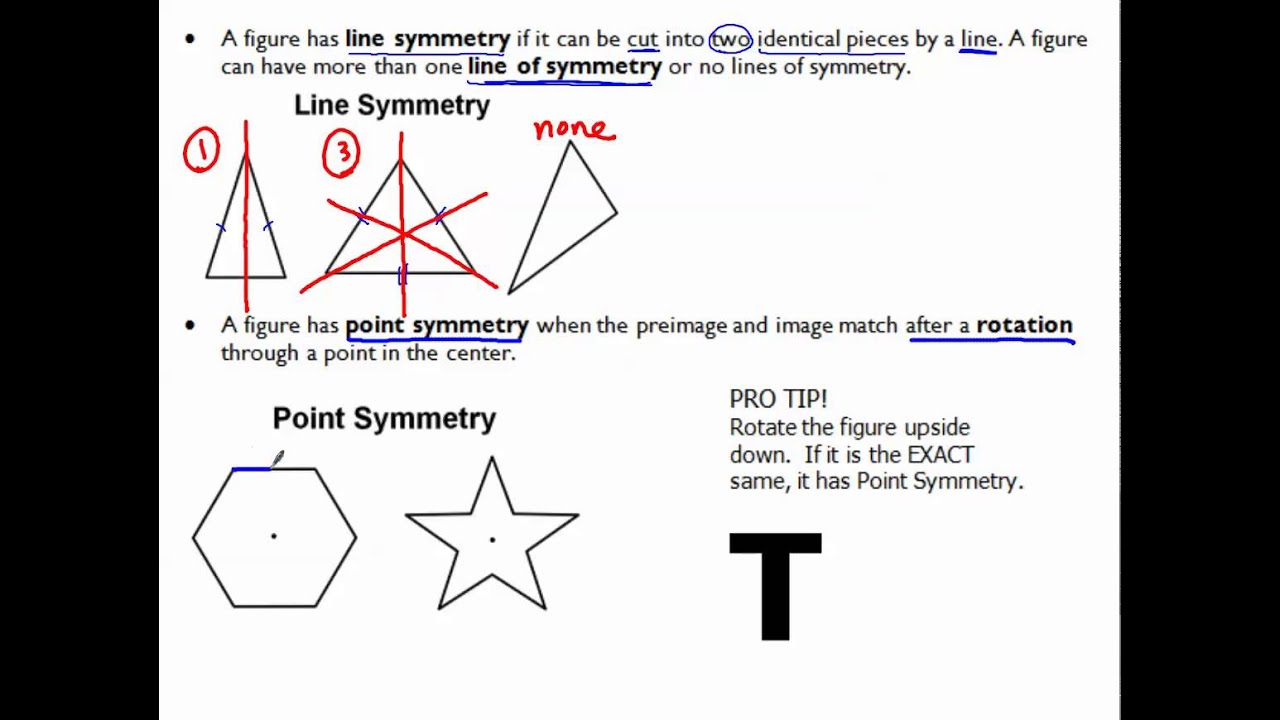
Point Symmetry. Point Symmetry is when every part has a matching part: the same distance from the central point. but in the opposite direction. It is also the same as "Rotational Symmetry of Order 2". Note: Point Symmetry is sometimes called Origin Symmetry, because the "Origin" is the central point about which the shape is symmetrical.

Symmetry Definition, Types, Examples (2022)
So, a function can never be symmetrical around the x-axis. Just remember: symmetry around x-axis ≠ function. To answer your second question, "even" and "odd" functions are named for the exponent in this power function: f (x) = xⁿ. - if n is an even integer, then f (x) is an "even" function. - if n is an odd integer, then f (x) is an "odd.

Symmetry Definition Solved Examples Geometry Cuemath
What is Point Symmetry? A figure has point symmetry if it has a rotational symmetry of 180 degrees. One way to check if a figure has point symmetry would be to turn it upside down. If the figure looks the same as the original then it has point symmetry. The following figures have point symmetry:
Point Symmetry Definition, Examples, and Diagram
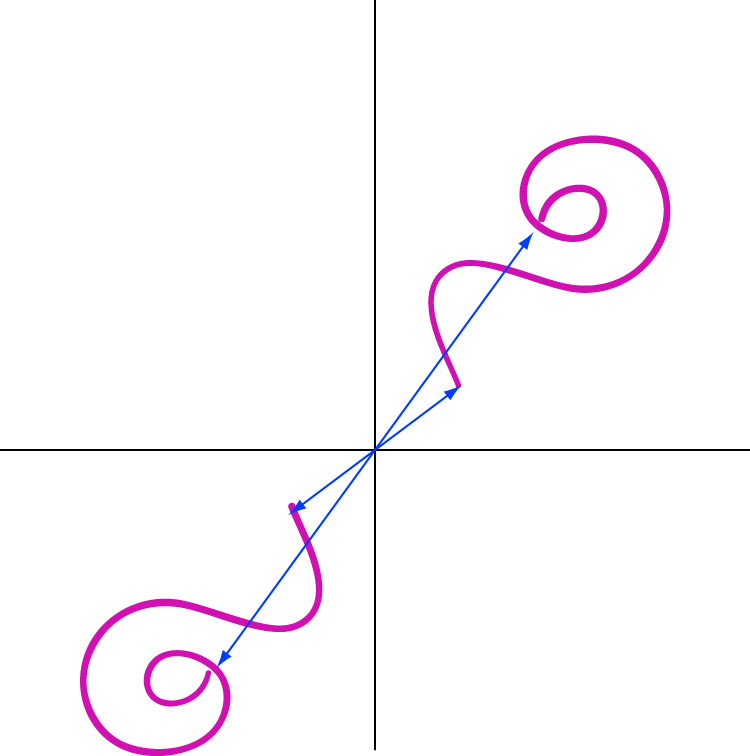
A special center point for certain kinds of symmetric figures or graphs . If a figure or graph can be rotated 180° about a point P and end up looking identical to the original, then P is a point of symmetry. Example: This is a graph of the curve together with its point of symmetry (-2, 1). The point of symmetry is marked in red.

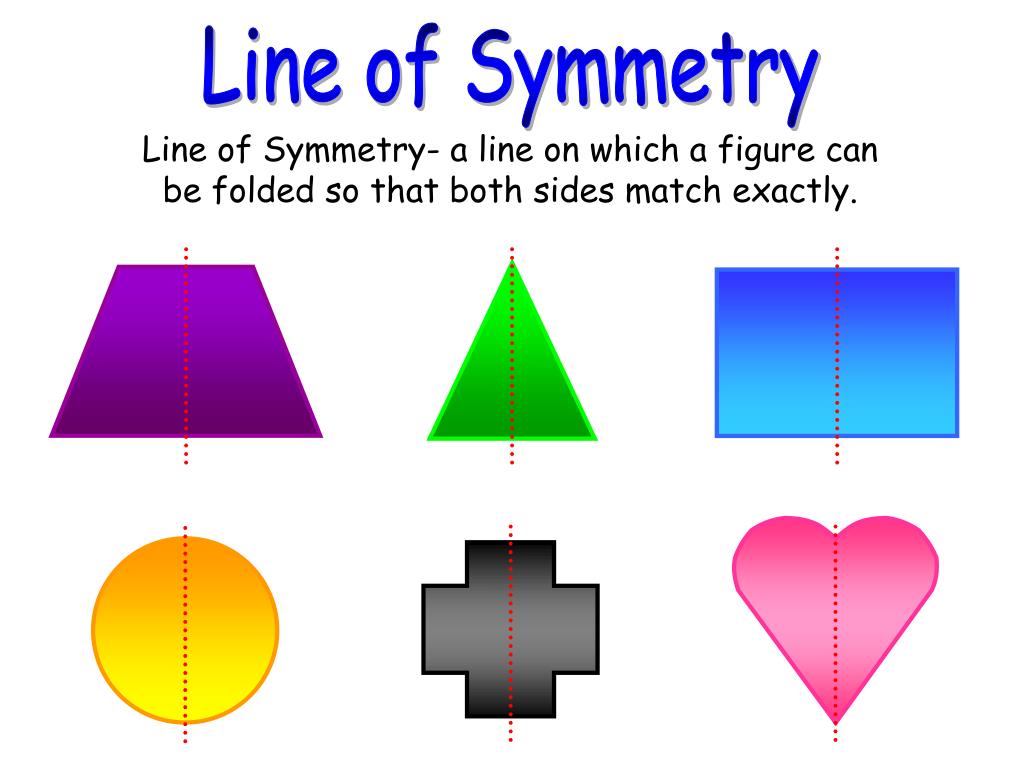
Line of Symmetry of Regular Polygon [with Formula and Examples]
Point Symmetry, or Origin Symmetry, or Central Symmetry is a type of symmetry where an object or shape looks the same when rotated 180° (a half-turn) around a central point. In this article, we will discuss Point Symmetry in detail including its definition, examples, as well as some real-life examples in nature as well.

Symmetry Definition Solved Examples Geometry Cuemath
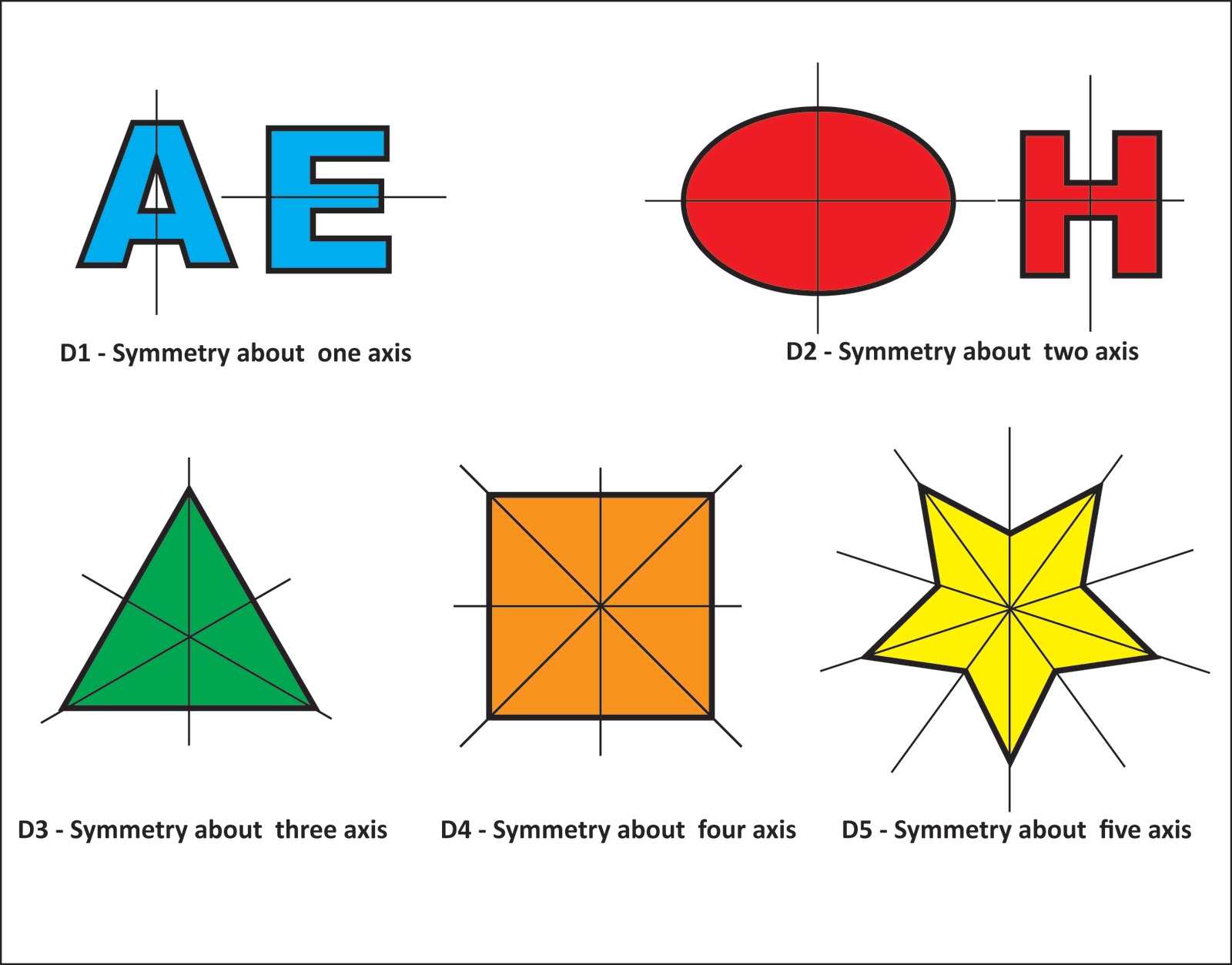
Symmetry describes when several parts of an object are identical, such that it's possible to flip, spin, and/or move the object without ultimately changing what it looks like. Symmetry is extremely powerful and beautiful problem-solving tool and it appears all over the place: in art, architecture, nature, and all fields of mathematics! The three basic kinds of 2-dimensional symmetry are.
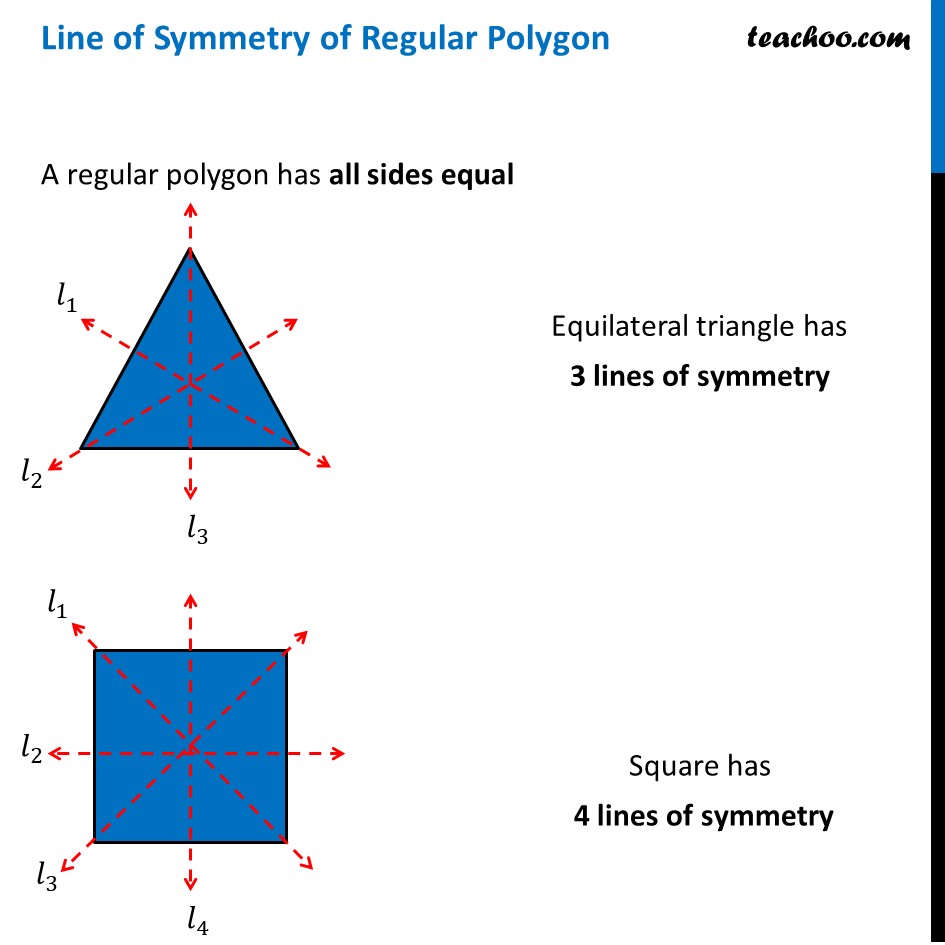
Line of Symmetry of Regular Polygon [with Formula and Examples]
Two points z and z^S in C^* are symmetric with respect to a circle or straight line L if all circles and straight lines passing through z and z^S are orthogonal to L. Möbius transformations preserve symmetry. Let a straight line be given by a point z_0 and a unit vector e^(itheta), then z^S=e^(2itheta)z-z_0^_+z_0, where z^_ is the complex conjugate.
Fun with Mathematics Symmetry in Art and Nature ( Part 1 of 3) Xplore & Xpress
Symmetry. In geometry, symmetry describes the balance a figure has. A figure or object has symmetry if a transformation (s) maps it back onto itself. Both plane and space figures may have symmetry. There are three basic types of symmetry: reflection, rotation, and point symmetry.

Symmetry in geometry YouTube
Point Symmetry. more. Where every part has a matching part the same distance from the central point but in the opposite direction. It looks the same when viewed from opposite directions (after a 180° rotation). Also called Origin Symmetry, and is identical to "Rotational Symmetry of Order 2". Illustrated definition of Point Symmetry: Where.

Lines and Points of Symmetry If there is a common point ofpehs. Symmetry Lines and Points of
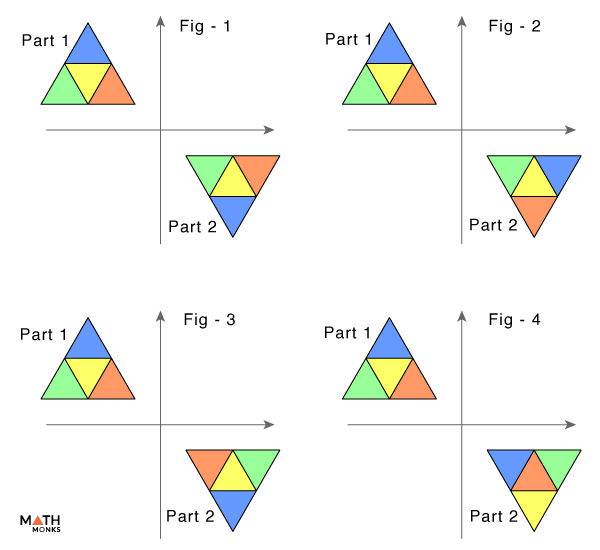
So, the point with which the rectangle is rotated is called the point of symmetry. Solved Example on Point of Symmetry Ques: Which of the figures has a point of symmetry? Choices: A. Graph 1 B. Graph 2 C. Graph 3 D. none of the above Correct Answer: A. Solution: Step 1: A figure or a graph when rotated by 180° looks similar to its original, it.
PPT Symmetry PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2505697
A figure has point symmetry, if it has a rotational symmetry of 180 degrees. One way to check if a figure has symmetry about a point would be to turn it upside down. If the figure looks the same as the original then it has symmetry about a point. Symmetry about a point is sometimes called Origin Symmetry, because the "Origin" is the central.
