
SF4 Lewis structure, Molecular geometry, Bond angle, Hybridization
Step #1: Calculate the total number of valence electrons. Here, the given molecule is SF4. In order to draw the lewis structure of SF4, first of all you have to find the total number of valence electrons present in the SF4 molecule. (Valence electrons are the number of electrons present in the outermost shell of an atom).
Lewis Structure Of Sf4 slidesharetrick
Sulfur tetrafluoride is the chemical compound with the formula S F 4.It is a colorless corrosive gas that releases dangerous HF upon exposure to water or moisture. Despite these unwelcome characteristics, this compound is a useful reagent for the preparation of organofluorine compounds, some of which are important in the pharmaceutical and specialty chemical industries.

How to draw SF4 Lewis Structure? Science Education and Tutorials
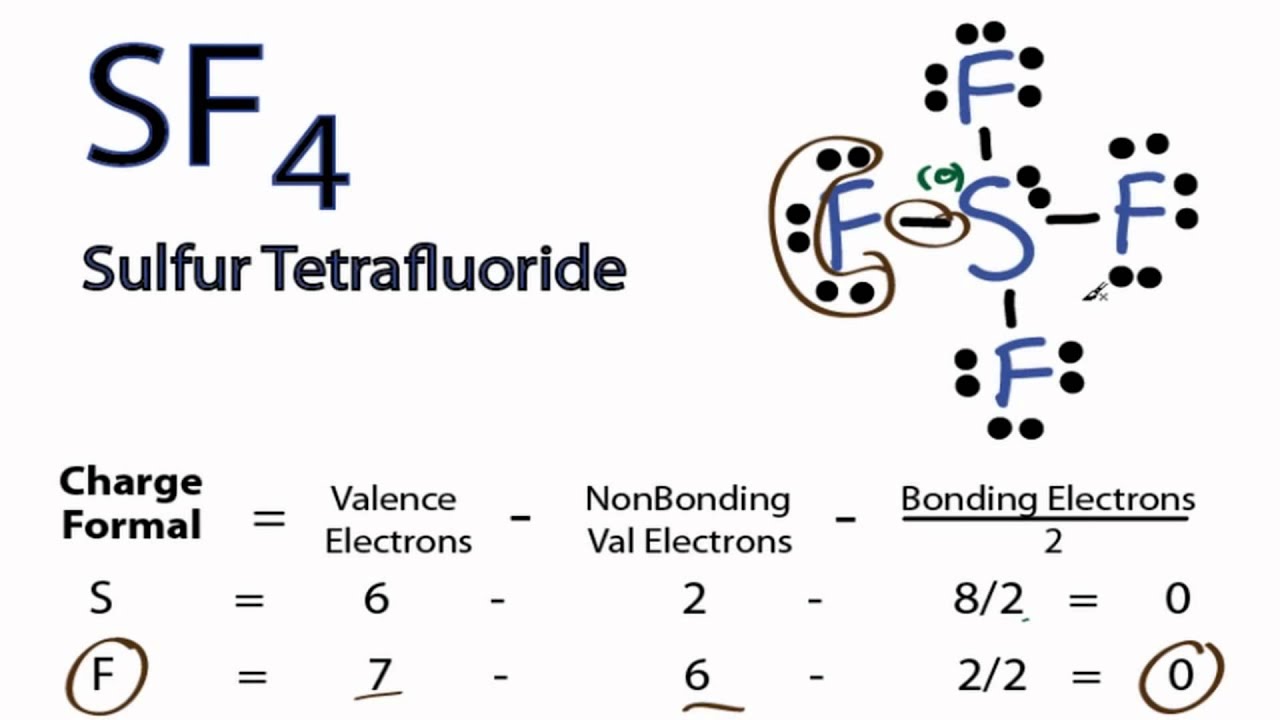
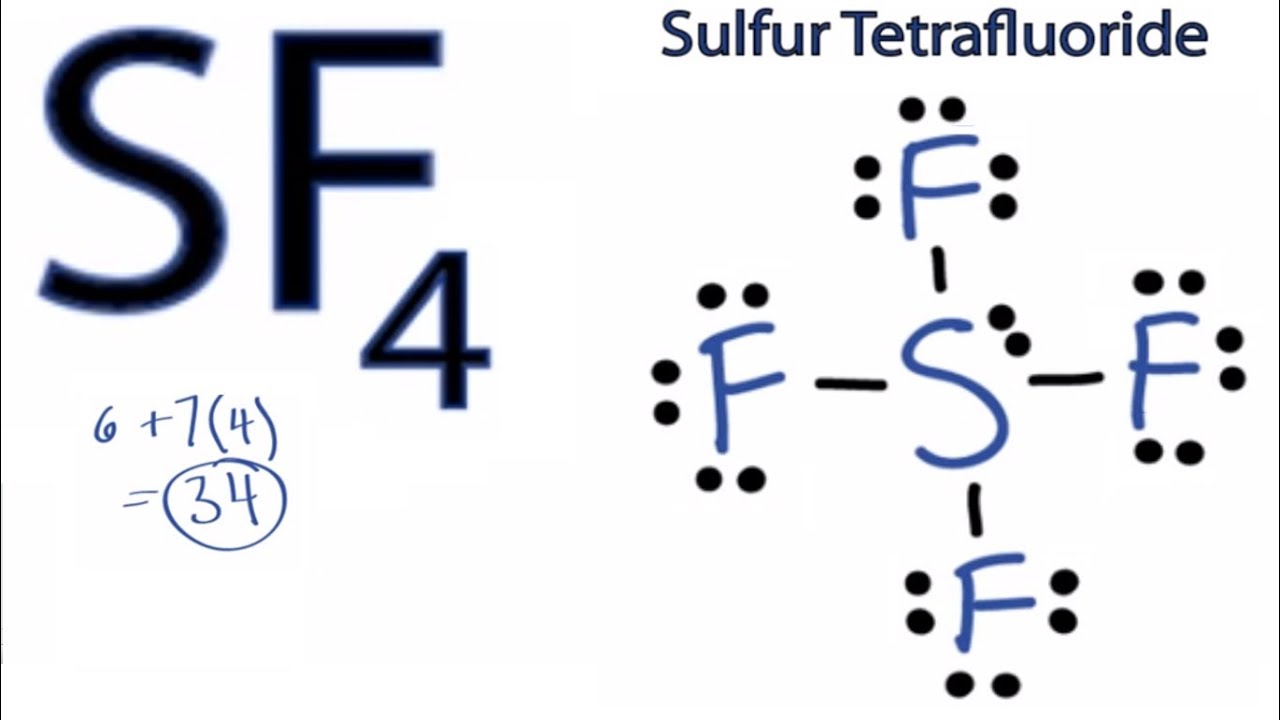
Drawing the Lewis Structure for SF 4. Viewing Notes: SF 4 is Lewis structure with Sulfur (S). Remember that Sulfur can hold more than 8 valence electrons.. Let's do the SF4 Lewis structure. On the periodic table, 6 valence electrons for Sulfur, 7 for Fluorine but we have 4 Fluorines; for a total of 34 valence electrons. We'll put the S, the.
SF4 Lewis Structure How to Draw the Lewis Structure for SF4 YouTube
The SF4 Lewis structure refers to the arrangement of atoms and electrons in a molecule of sulfur tetrafluoride. In this structure, there is one sulfur atom bonded to four fluorine atoms. The Lewis structure helps us understand the bonding and electron distribution in a molecule. It shows the connectivity of atoms and the placement of lone pairs.

How to draw Sf4 Lewis Structure? Beginners Guide
Sulfur tetrafluoride (SF4) Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry or shape, electron geometry, bond angle, formal charge. SF 4 is the chemical formula for sulfur tetrafluoride, a colorless gas with a distinct rotten-egg-like odor. Its molar mass is 108.4 g/mol thus it is heavier than air. Sulfur tetrafluoride is a highly toxic gas that can.

Sf4 Polar or Nonpolar
In SF4 lewis structure, each fluorine atom has joint with center sulfur atom. Also, there is a lone pair on sulfur atom. Sulfur has a valence of 6. Therefore sulfur becomes the center atom. In this tutorial, we will learn how to draw the lewis structure of SF4 step by step.

Is SF4 Polar or Nonpolar? Techiescientist
You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Question: The Lewis structure for SF4 is shown. What is the electron-pair geometry and the molecular geometry around the central atom? The Lewis structure for SF4 is shown. What is the electron-pair geometry and the molecular geometry around the.

SF4 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, and MO Diagram Techiescientist
The Lewis structure helps one to understand the sharing of electrons between the central and neighboring atoms within a compound. Here the central atom is Sulfur and the neighboring atoms are Fluorine. This is the general idea of how and why Lewis structures are made. SF4 Lewis Structure. Let us look at how SF4's Lewis structure can be formed.
SF4 Molecular Geometry / Shape YouTube
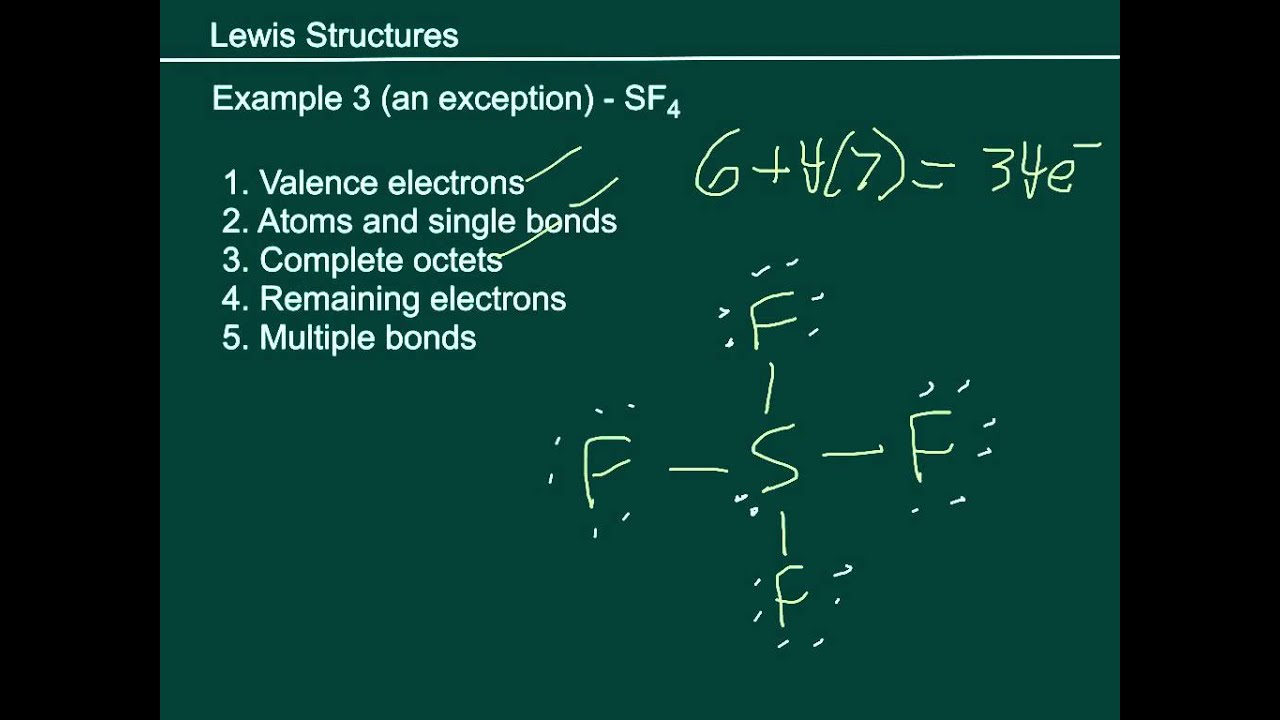
I quickly take you through how to draw the Lewis Structure of SF4, Sulfur TetraFluoride. I also go over formal charge, hybridization, shape and bond angle.**.
Basic Lewis Structures SF4 YouTube
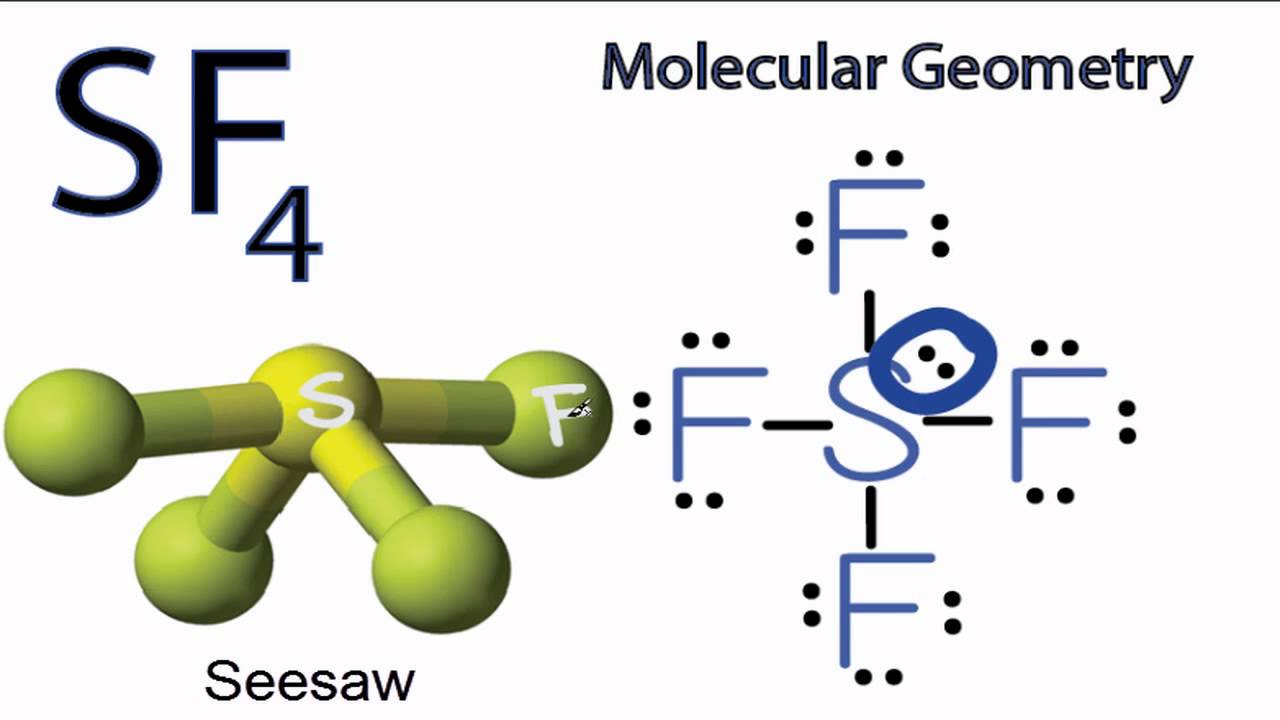
Lewis structure is used to show the bond formation in sulfur tetrafluoride. Sulfur is the least electronegative of the two. So, it will lie at the center of the molecule. Dash lines represent the four S-F single covalent bonds. Dots represent the lone pairs. VSEPR theory is used to predict the shape of the SF 4 molecule. According to this.

SF4 Lewis Structure How to Draw the Lewis Structure for SF4 YouTube
To draw the Lewis structure of SF4, we follow a step-by-step process. First, we arrange the atoms, then distribute the valence electrons, and finally, place them around the atoms to form bonds and lone pairs. 1. Determine the Total Number of Valence Electrons. To begin, count the total number of valence electrons in the SF4 molecule.
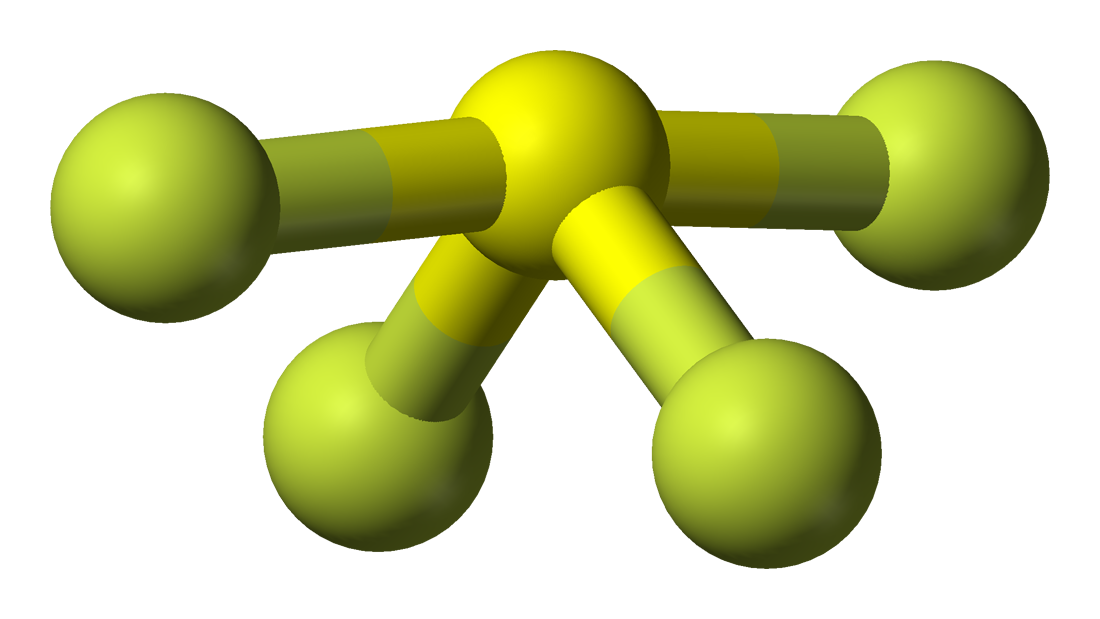
SF4 Molecular Geometry, Lewis Structure, Bond Angles and Polarity
The SF4 Lewis structure is a diagram that illustrates the number of valence electrons and bond electron pairs in the SF4 molecule. The geometry of the SF4 molecule can then be predicted using the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR Theory), which states that molecules will choose the SF4 geometrical shape in which the electrons.

SF4 Lewis Structure ,Valence Electrons,Formal Charge,Octet Rule
For the SF4 Lewis structure use the periodic table to find the total number of valence electrons for the SF4 molecule. Once we know how many valence electrons there are in SF4 we can distribute them around the central atom with the goal of filling the outer shells of each atom. Note that Sulfur is the least electronegative element in the SF4.

SF4 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, and MO Diagram Techiescientist
Hello Guys!Today we are going to look at the Lewis Structure of SF4 ( Xenon Tetrafluoride )The Sulphur atom has six valence electrons in its outer shell and.
[Solved] Draw the Lewis structure of SF 4 showing all lone pairs. Identify... Course Hero
Steps of drawing SF4 lewis structure Step 1: Find the total valence electrons in SF4 molecule. In order to find the total valence electrons in SF4 molecule, first of all you should know the valence electrons present in sulfur atom as well as fluorine atom. (Valence electrons are the electrons that are present in the outermost orbit of any atom.). Here, I'll tell you how you can easily find.

SF4 Molecular Geometry Science Education and Tutorials
SF4 Lewis Structure. Lewis structure is a pictorial representation of the bonds and valence electrons in the molecule. The bonds formed between two atoms are depicted using lines, whereas the valence electrons not forming any bonds are shown by dots. The valence electrons that participate in forming bonds are called bonding pairs of electrons.
