Volcanoes
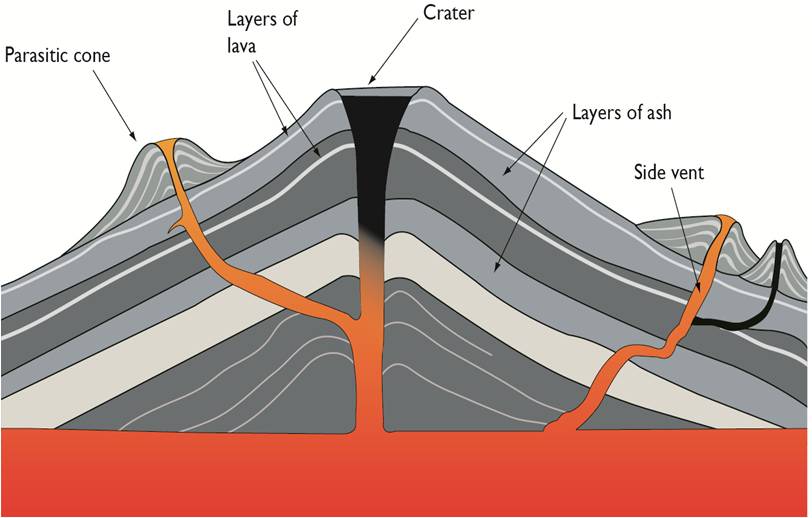
compound volcano Volcanic massif formed from coalesced products of multiple, closely spaced, vents. debris avalanche Catastrophic landsliding of gravitationally unstable volcano flanks resulting in a widely dispersed deposit at the foot of the edifice, typically characterized by a hummocky surface. edifice Constructional volcanic mass.

8.3 Types of Volcanoes Principles of Earth Science
Schematic diagram of a composite volcano. Credit: NPS illustration by Trista Thornberry-Ehrlich (Colorado State University). Right image Diagram with feature labels. Credit: NPS illustration by Trista Thornberry-Ehrlich (Colorado State University). Glossary—Cinder Cone Volcanoes Ash Cinder

Diagram Of Volcano Eruption
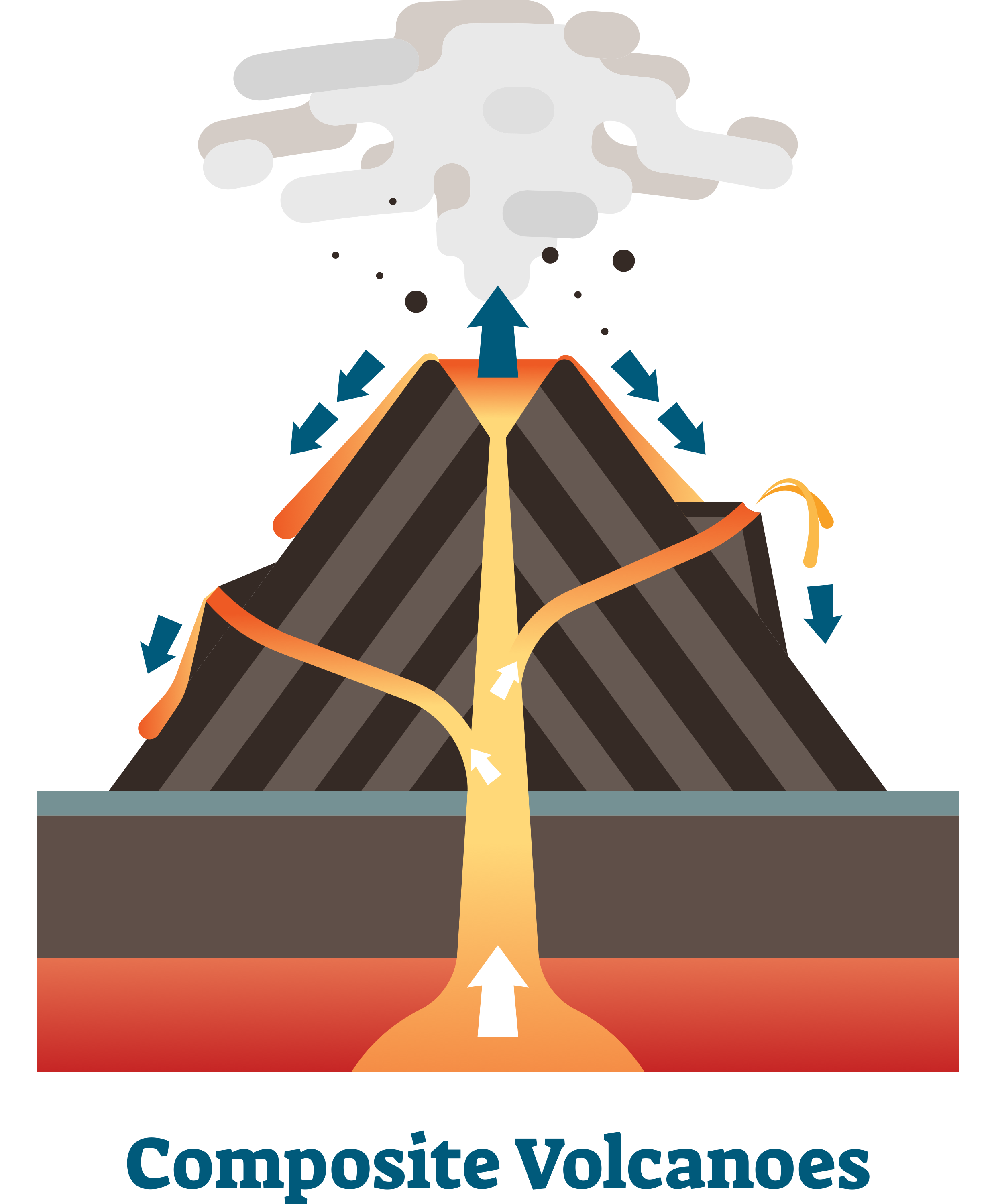
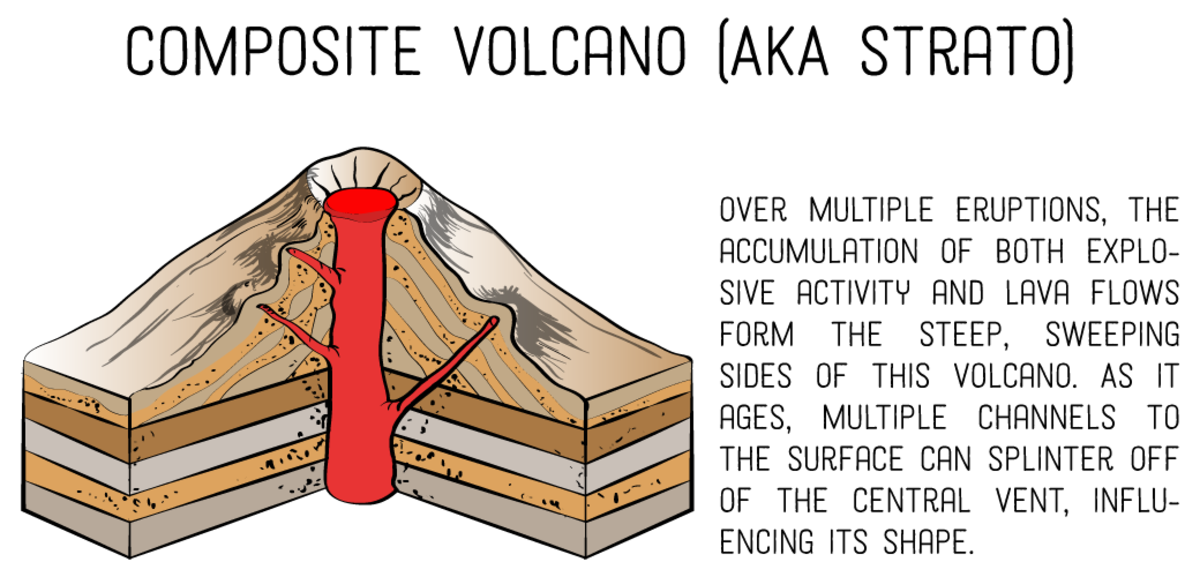
A composite volcano, also known as a stratovolcano is a cone-shaped volcano built from several layers of lava, pumice, ash, and tephra. Due to its viscous lava, a composite volcano tends to form tall peaks rather than rounded cones. Mount Fuji in Japan and Mount Shasta in California are examples of composite volcanoes.
39 composite cone volcano diagram Diagram Resource
The diagram is intended for illustrative purposes rather than a rigorous classification. The composite volcanoes discussed in this article are constructional features, each with a reasonably protracted history of eruptions.. Composite cones are commonly taken as synonymous with stratovolcanoes; the latter term is preferred in many.
What is a Stratovolcano Cone)? Earth How
There are 3 types of volcanoes: Stratovolcanoes. Shield volcanoes. Cinder cones. Let's dive into the differences between these types of volcanoes. 1. Stratovolcanoes (Composite Cones) Stratovolcanoes are tall and cone-shaped. Instead of flat shield volcanoes like in Hawaii, they have bigger peaks.

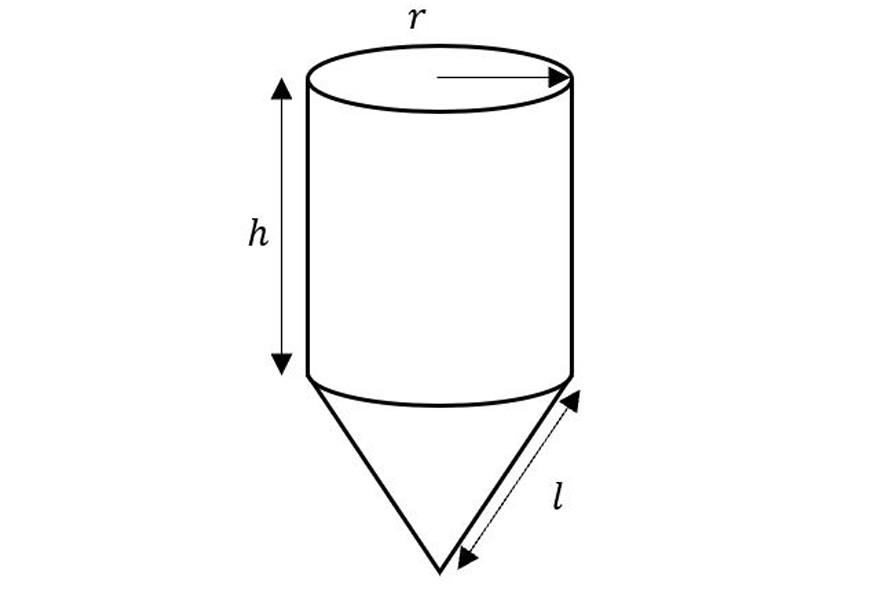
Consider this composite figure made of a cone and a cylinder. what is
Shield volcano cutaway diagram . Explosive Eruptions. Explosive eruptions occur where cooler, more viscous magmas (such as andesite) reach the surface.. These eruptions build up more steeply-sloping Composite volcanoes like this one in Chile.. Composite volcano, Andes, Chile. Composite cone diagram . Accessibility; Terms & Conditions.
Part 5 Surface Area The Beginner's Guide to Year 9 Maths
Mt. Kilauea in Hawaii is a good example of a shield volcano. Mt. Kilauea, Hawaii Composite cones Some volcanoes produce different types of eruptions. Sometimes there are massive ash eruptions which produce layers of ash. At other times there are eruptions of lava which produce layers of lava.
39 composite cone volcano diagram Diagram Resource
Composite volcanoes are the most common type of volcano on the Earth's surface. They account for 60 percent of the Earth's volcanism. Most of the remaining 40 percent occurs under the oceans. Composite volcanoes consist of alternating layers of ash and lava flows. Known also as strato volcanoes, their shape is a symmetric cone with steep.
39 composite cone volcano diagram Diagram Resource
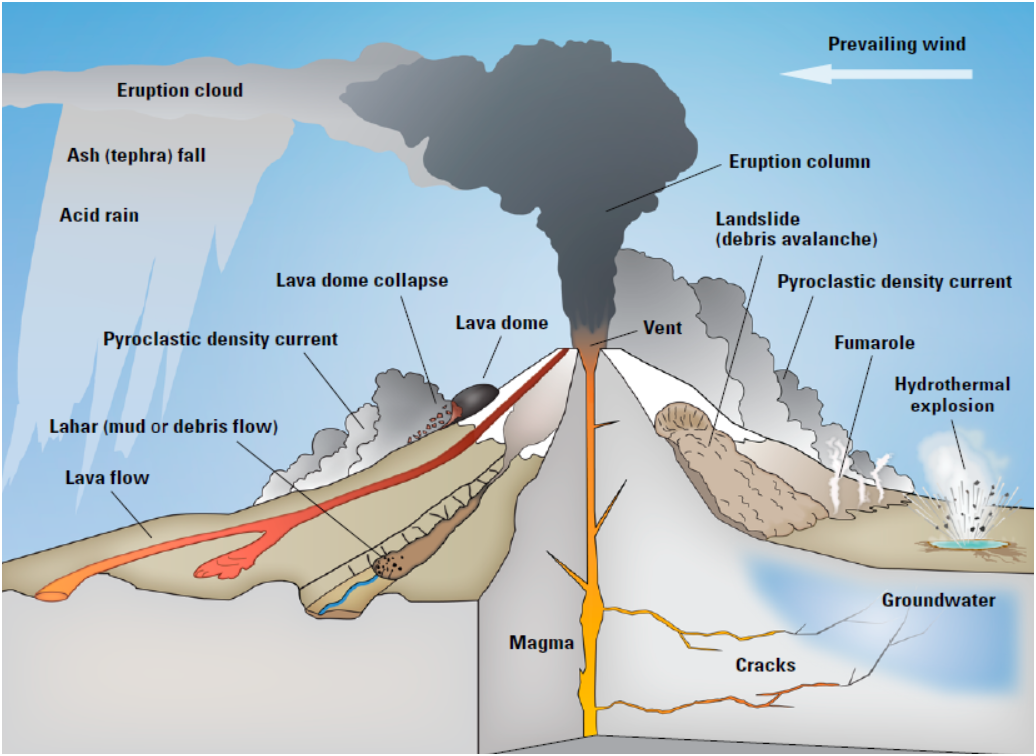
stratovolcano, volcanic landform characterized by a conical shape formed by layers of volcanic material deposited during successive volcanic eruptions.Stratovolcanoes tend to slope gently at the base but rise quickly near the summit to form tall mountain peaks. They are typically found above subduction zones, and they are often part of large volcanically active regions, such as the Ring of.

Cone Cuemath
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a conical volcano built up by many layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. [1]

PPT melting PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Stratovolcanoes, also known as composite cone volcanoes, erupt viscous lava that forms a steep-sided, triangular-shaped structure. BGS ©UKRI.

39 composite cone volcano diagram Diagram Resource
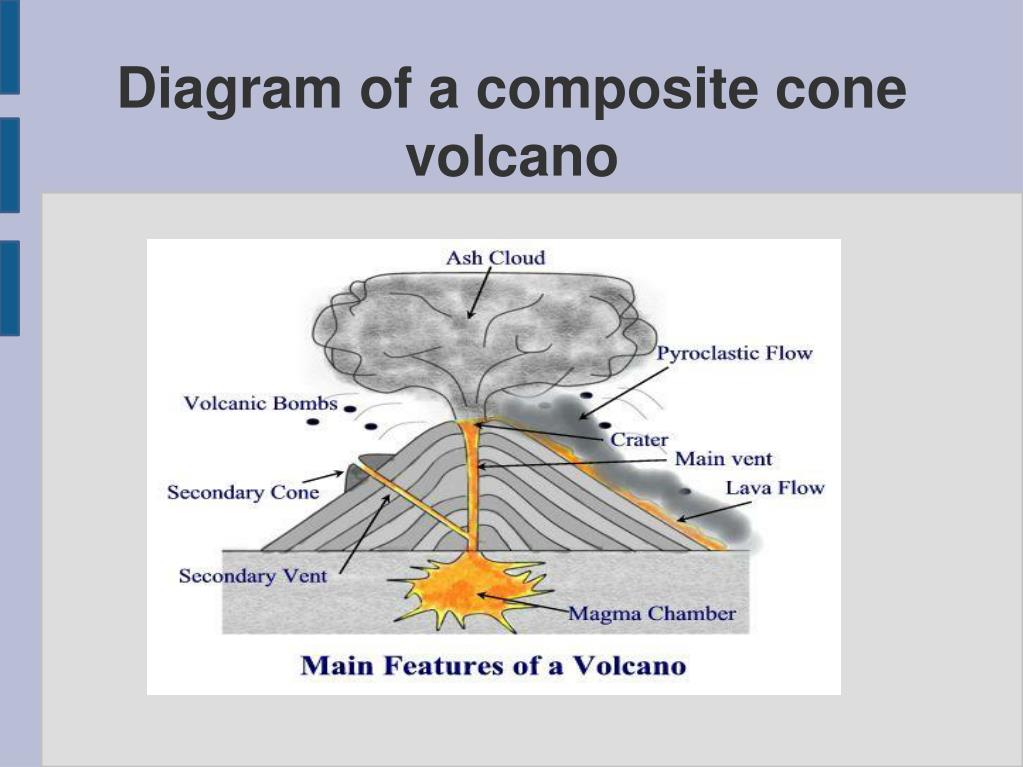
Article Vocabulary A volcanic cone is a hill-shaped landform that forms around a volcano. Volcanic cones can be steep or gently sloping depending on the type of eruption that forms them. The steepest cones form around cinder cone volcanos.

Diagrams Of Composite Volcanoes
Composite cones are large volcanoes (many thousands of feet or meters tall) generally composed of lava flows, pyroclastic deposits, and mudflow (lahar) deposits, as well as lava domes. Composite volcanoes are active over long periods (tens to hundreds of thousands of years), and erupt periodically.

39 composite cone volcano diagram Diagram Resource
The cinder cone started explosively shooting cinders out of the vent in the middle of a farmer's field. The volcanism quickly built up the cone to a height of over 90 m (300 ft) within a week and 365 m (1,200 ft) within the first 8 months. After the initial explosive eruption of gases and cinders, basaltic lava poured out from the base of the.
PPT EXTRUSIVE VOLCANIC FEATURES First Form Prepared by Mrs. L
A volcanic cone is a triangle-shaped hill formed as material from volcanic eruptions piles up around the volcanic vent, or opening in Earth's crust. Most volcanic cones have one volcanic crater, or central depression, at the top. They are probably the most familiar type of volcanic mountain. Major Types of Volcanic Cones Composite cones

Creative Segmented 3D Cone Diagrams for PowerPoint SlideModel
Principal Types of Volcanoes Geologists generally group volcanoes into four main kinds--cinder cones, composite volcanoes, shield volcanoes, and lava domes. Cinder cones C inder cones are the simplest type of volcano. They are built from particles and blobs of congealed lava ejected from a single vent.
