
Image result for rl circuit formula
Figure 3.6.1 3.6. 1: Series RLC Circuit. We will assume that the voltage source is an audio oscillator that produces the voltage. V(t) = A cos(ωt +φ) V ( t) = A cos ( ω t + φ) We represent this voltage as the complex signal. V(t) ↔ Aejφejωt V ( t) ↔ A e j φ e j ω t. and give it the phasor representation.

ANALYSIS OF RL, RC & RLC CIRCUIT YouTube
RC, RL and RLC Circuits . 0. 2 4 6 8 10 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 18 20 t V V0 1/2 V0 T1/2 Figure 4: Discharge of a capacitor. Procedure y Assemble the circuit shown in Figure 5. Function Generator. Oscilloscope R = 10 kΩ C = 0.1 μF Red Black Red Black Figure 5: Investigating an RC circuit . y With initial values R = 10 kΩ, C = 0.1 µF, and f = 100.

RLC Circuits (13 of 19) Summary of RLC Circuit Analysis YouTube
Time Constant τ "Tau" Equations for RC, RL and RLC Circuits. Time constant also known as tau represented by the symbol of " τ" is a constant parameter of any capacitive or inductive circuit. It differs from circuit to circuit and also used in different equations. The time constant for some of these circuits are given below:

Rl Rc Rlc Series And Parallel Circuits Circuit Diagram
An RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.. RC circuit; RL circuit.

Passive Components in AC Circuits with Equations Electrical Academia
Basic Principle of RC/RL and RLC circuits: Before we start with each topic let us understand how a Resistor, Capacitor and an Inductor behave in an electronic circuit. For the purpose of understanding let us consider a simple circuit consisting of a capacitor and resistor in series with a power supply (5V). In this case when the power supply is.

Time Constant τ “Tau” Formulas for RC, RL & RLC Circuits Time constant, Circuit, Electronic
The transient response of RL circuits is nearly the mirror image of that for RC circuits. To appreciate this, consider the circuit of Figure 9.5.1 . Figure 9.5.1 : RL circuit for transient response analysis. Again, the key to this analysis is to remember that inductor current cannot change instantaneously.

EE269 RC, RL and RLC Circuits Part 1 EE269 Lab 2 (RC, RL, RLC Circuits) Part 1 This part
Experiment 6: Ohm's Law, RC and RL Circuits OBJECTIVES 1. To explore the measurement of voltage & current in circuits 2. To see Ohm's law in action for resistors 3. To explore the time dependent behavior of RC and RL Circuits PRE-LAB READING INTRODUCTION When a battery is connected to a circuit consisting of wires and other circuit elements
What Is The Power Factor Of Rl Circuit Wiring Diagram
Goal: Measure the time constant of an RC and an RL circuit, compare to the theoretical calculations. Use the schematics of figure 2 and 3 as your circuits. Figure 3: R-L circuit driven by an ideal step Voltage source. V IN can undergo a step change from zero to V IN or from V IN to zero Procedure: a.
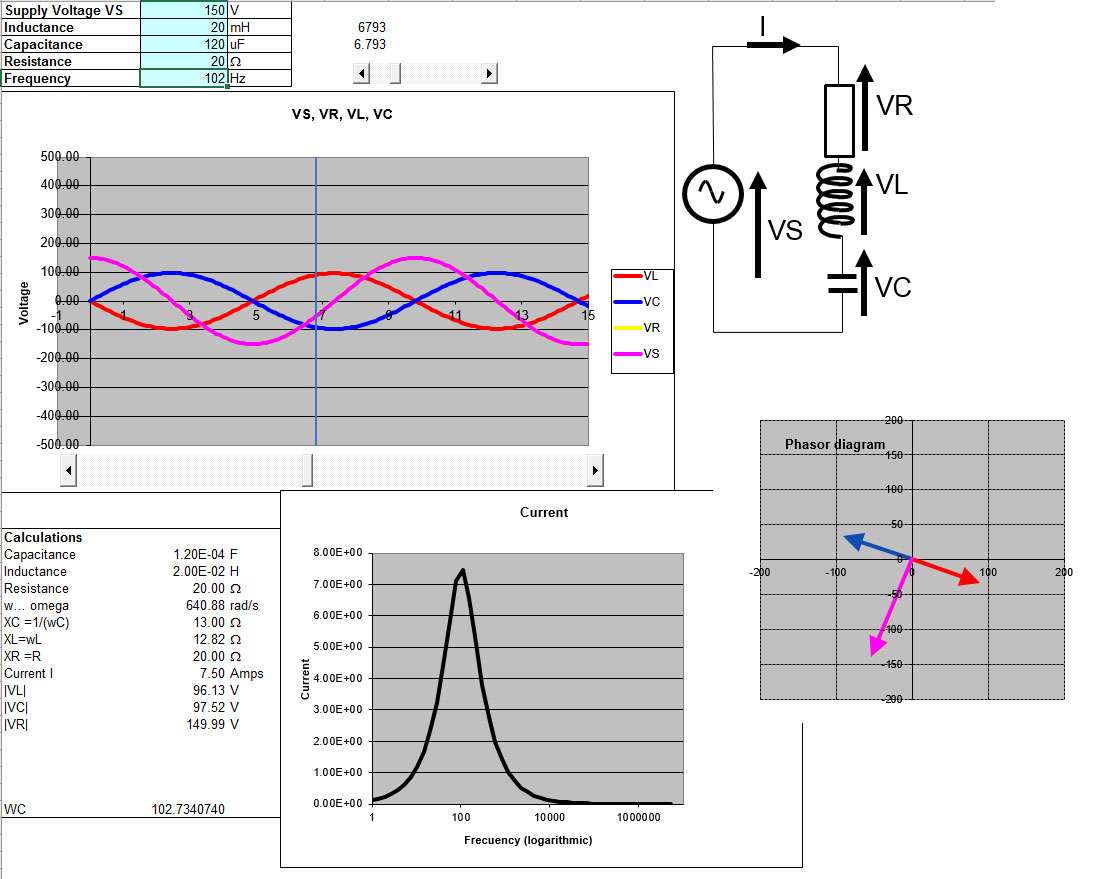
AllSingingAllDancing RLC circuit Engineering Teaching
The RLC circuit analyzed here is the parallel form. The solution to the natural response emerges from this long analysis. The answer is not a simple single exponential equation like we get for RC, but rather a choice of three different responses ("variations") depending on the value of R, L , and C.
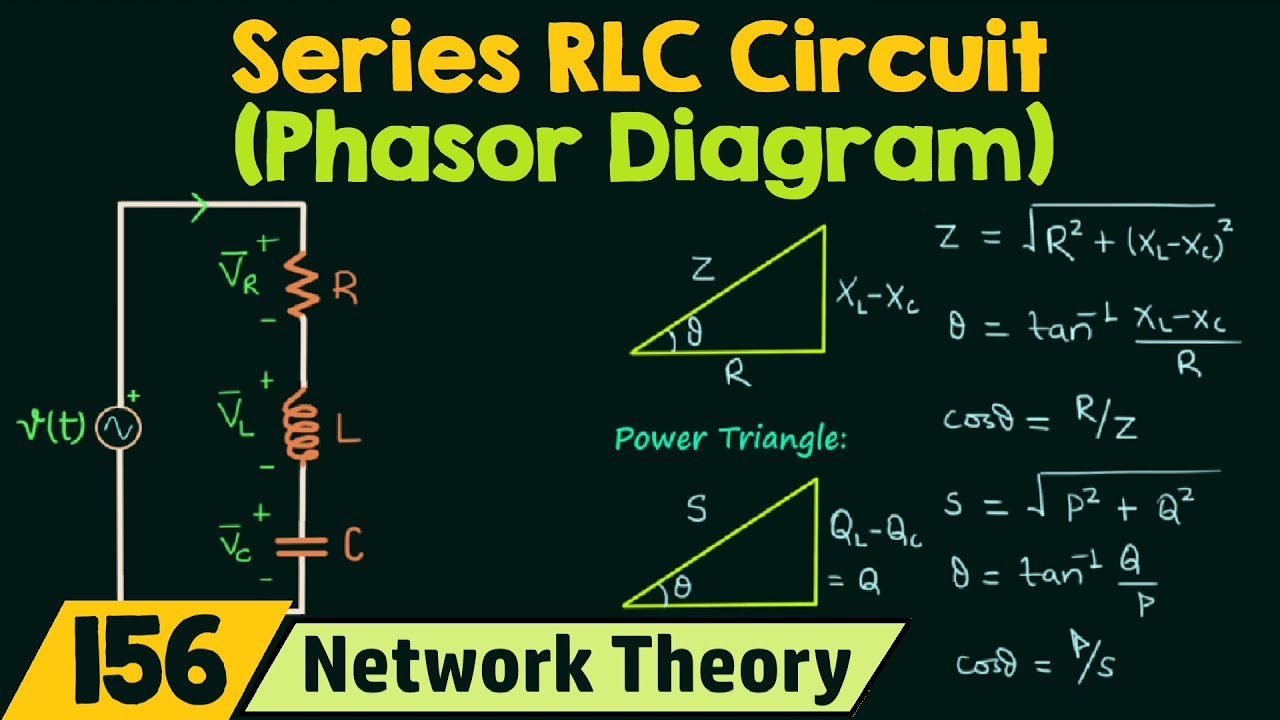
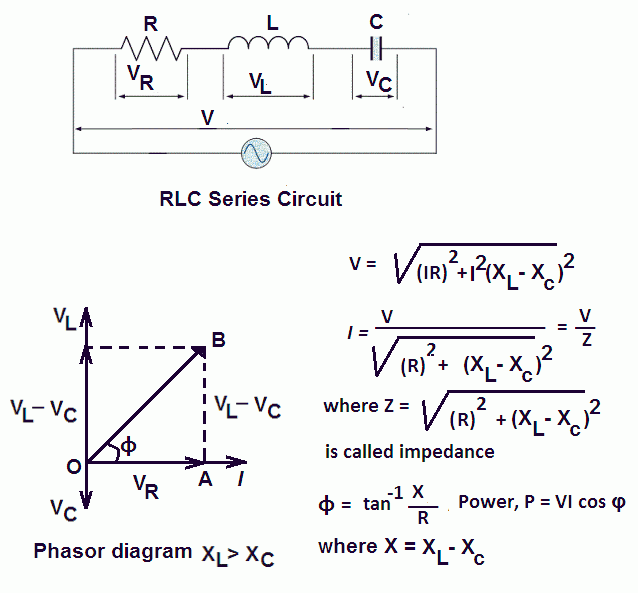
Phasor Diagram For Rlc Series Circuit Circuit Diagram www.vrogue.co
RC, RL, and RLC Circuits 5 Procedure • Measure the half-life, T 1/2 and from this compute the time constant τ using Equation 3. • Compute the value of RC from component values. Note that, as described above, the square-wave generator has an internal resistance of 50 Ω. Thus

RL, RC, AND RLC CIRCUITS
Fig. 8.21 (a) A voltage-step function is shown as the source driving a general network. (a) A voltage-step forcing function is shown as the source driving a general network. (b) A simple circuit which, although not the exact equivalent of part (a), may be used as its equivalent in many cases. (c) An exact equivalent of part (a).
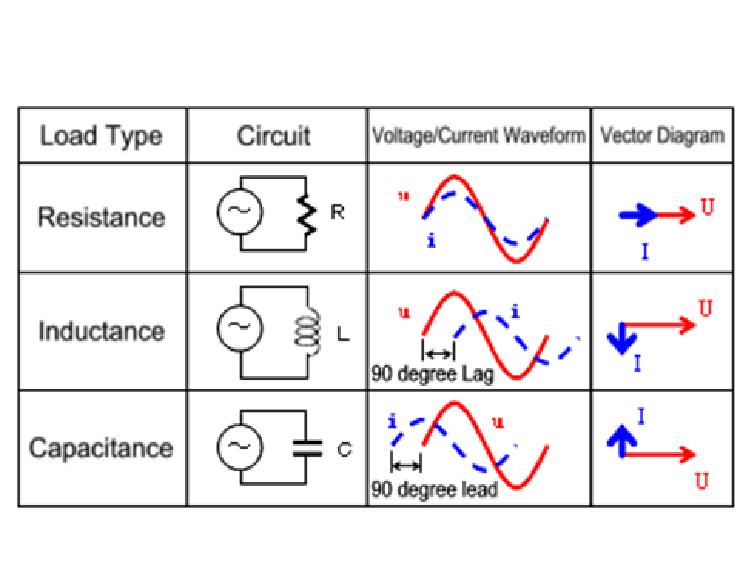
Offset problem in simulating current and voltage phase relation of parallel rlc circuit, Is it a
The LC circuit. In the limit R →0 the RLC circuit reduces to the lossless LC circuit shown on Figure 3. S C L vc +-+ vL - Figure 3 The equation that describes the response of this circuit is 2 2 1 0 dvc vc dt LC + = (1.16) Assuming a solution of the form Aest the characteristic equation is s220 +ωο = (1.17) Where 1 ο LC ω= The two roots are
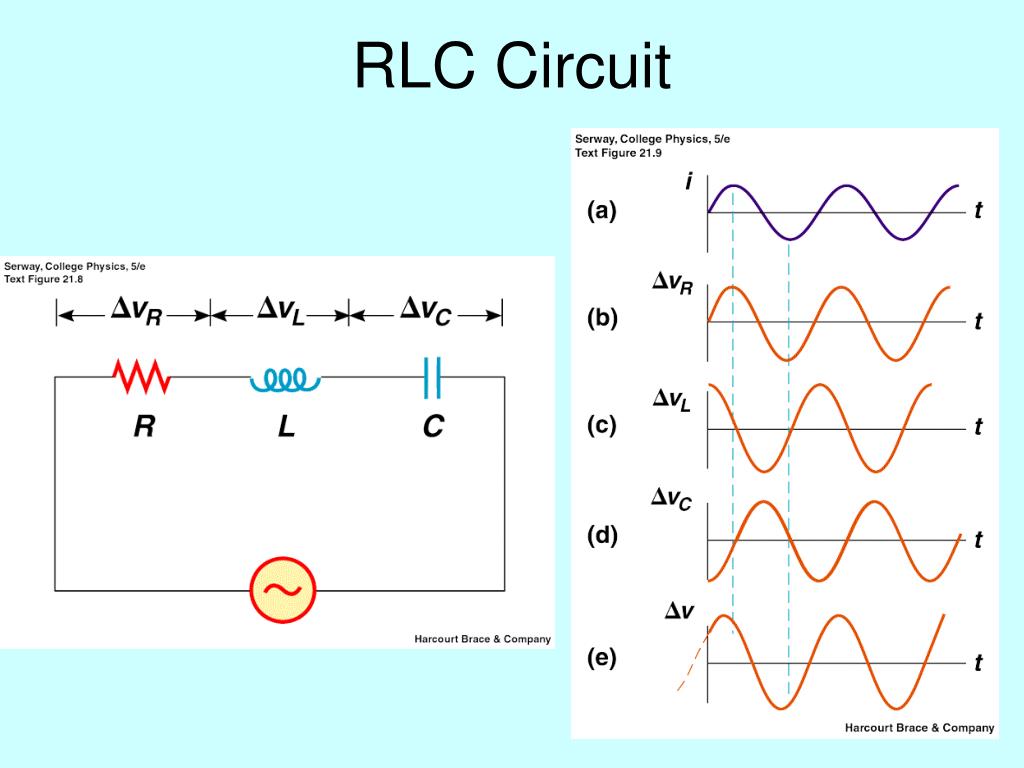
impedance of parallel rlc circuit
Learning Objectives. After completing this chapter, you should be able to: Identify series-only and parallel-only sub-groups in series-parallel RLC networks. Compute complex equivalent impedance for series-parallel RLC circuits. Simplify an entire RLC network into a simple series or parallel equivalent comprised of complex impedances.

RL, RC, and RLC Circuits Natural vs Forced Response
The Series RLC Circuit Impulse response of RC Circuit. Let's examine the response of the circuit shown on Figure 1. The form of the source voltage Vs is shown on Figure 2. Vs R C vc +-Figure 1. RC circuit t Vp 0 tp Vs Figure 2. We will investigate the response vc(t) as a function of the τp and Vp. The general response is given by: () 1 0 t.
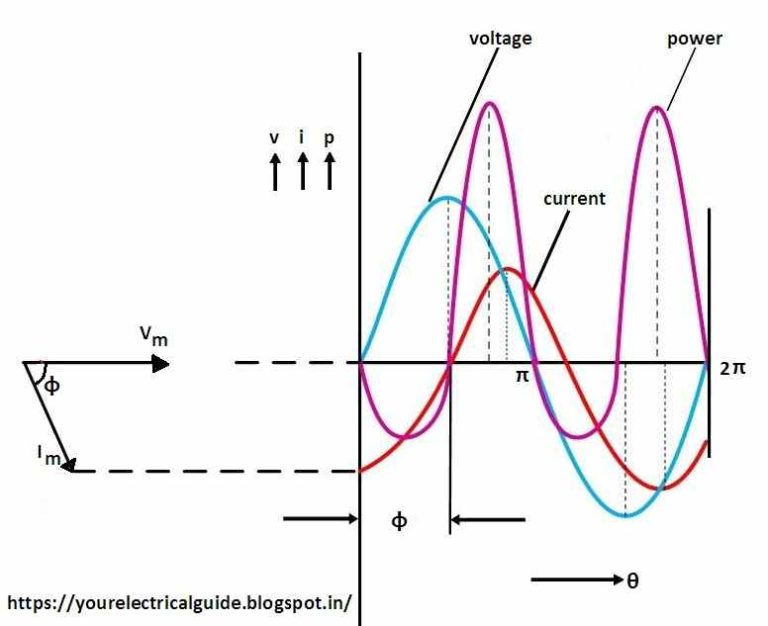
RC RLC RL Series Circuits Your Electrical Guide
7.1: Introduction to RL and RC Circuits - Engineering LibreTexts. search Search. build_circle Toolbar. fact_check Homework. cancel Exit Reader Mode. school Campus Bookshelves. menu_book Bookshelves. perm_media Learning Objects. login Login.

RC, RL and RLC Circuit Basic Principle and Circuit Explanations
Two-element circuits and uncoupled RLC resonators. RLC resonators typically consist of a resistor R, inductor L, and capacitor C connected in series or parallel, as illustrated in Figure 3.5.1. RLC resonators are of interest because they behave much like other electromagnetic systems that store both electric and magnetic energy, which slowly.
