Vitamin B10 Molecular Structure, 3d Model Molecule, 4aminobenzoic Acid, Structural Chemical
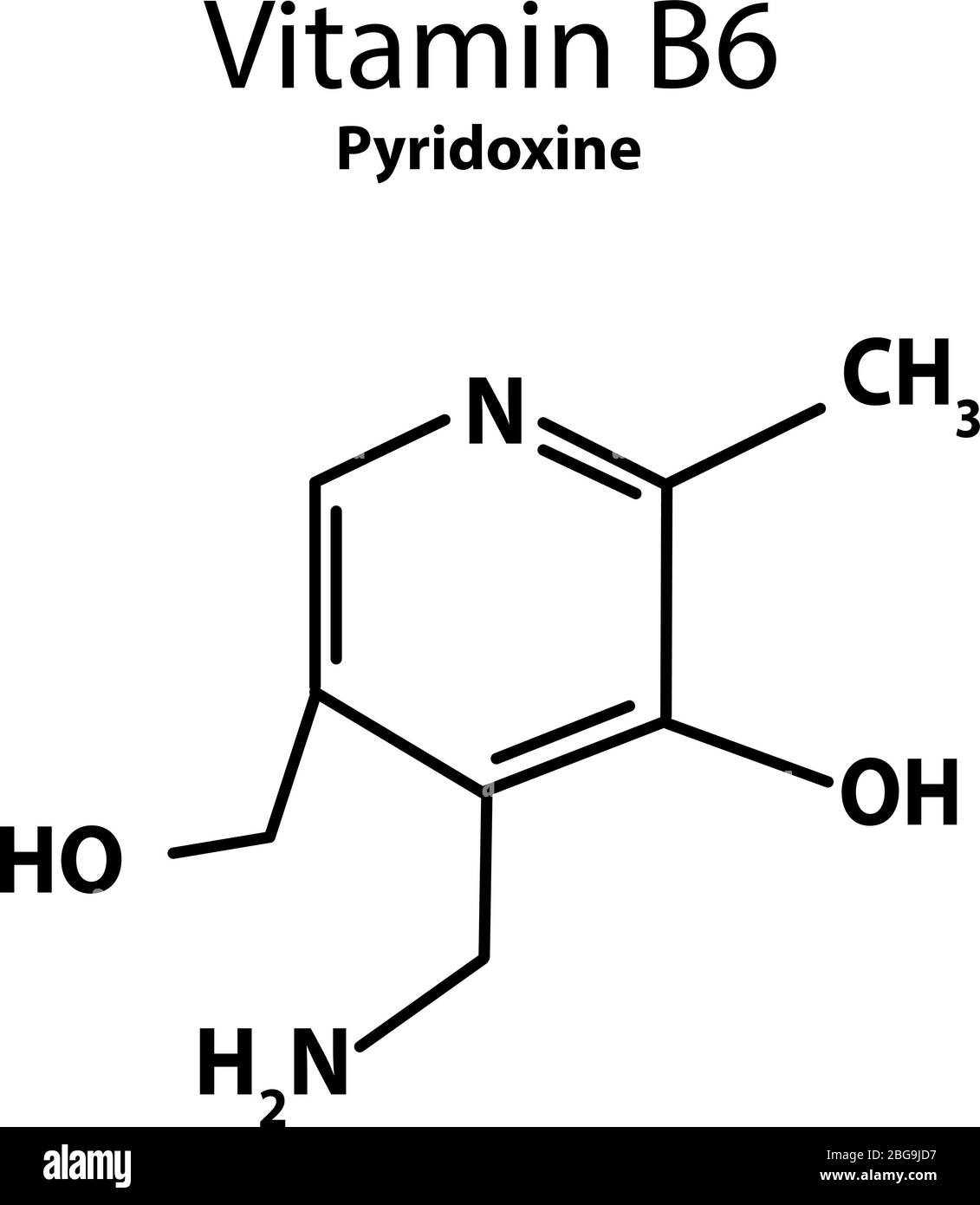
"Vitamin A" is the generic term for a group of fat-soluble compounds found in both animal and plant foods. Functions in your body Vitamin A is essential for your health. It supports cell.
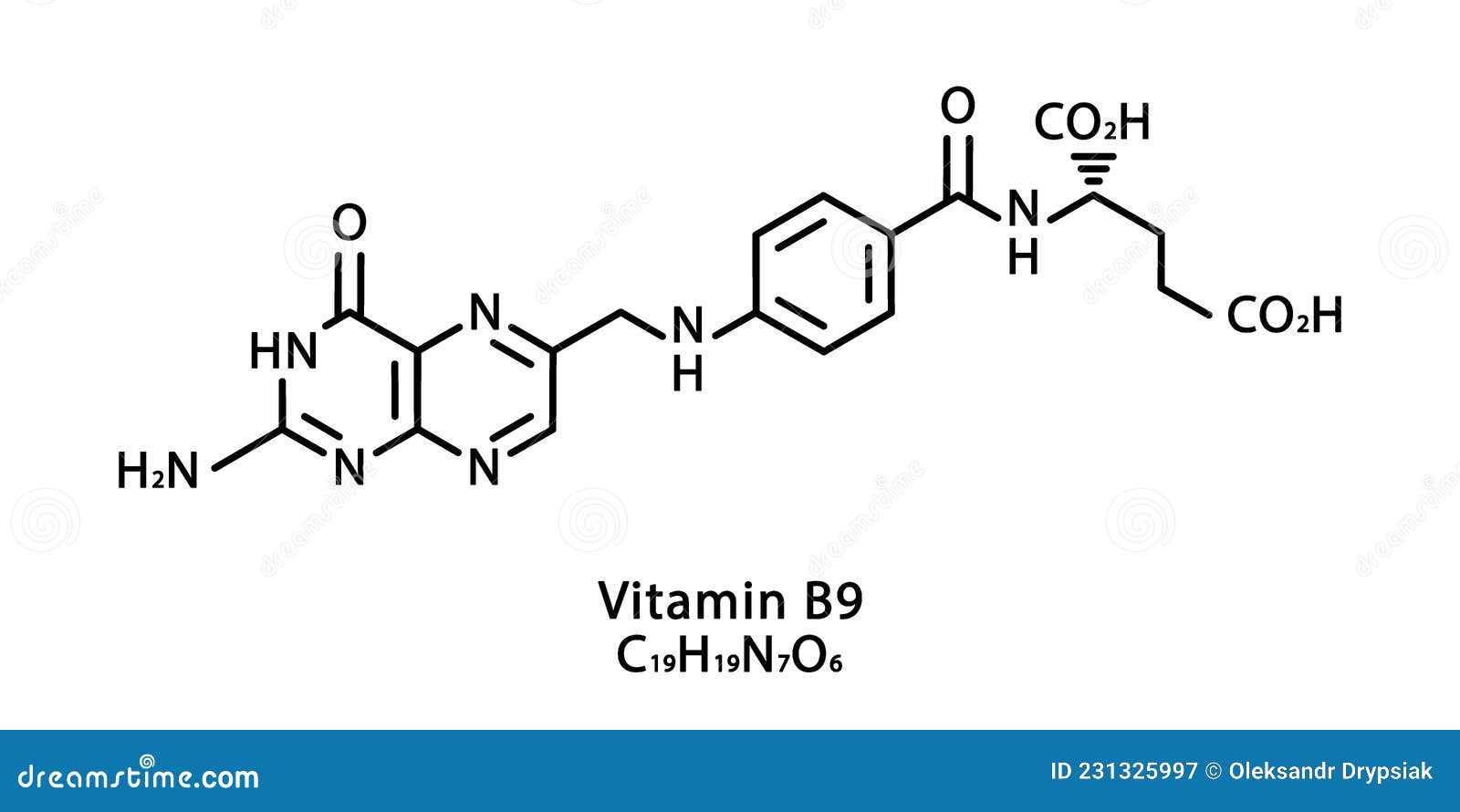
Vitamin B6. Pyridoxine Molecular chemical formula. Infographics. Vector illustration on isolated
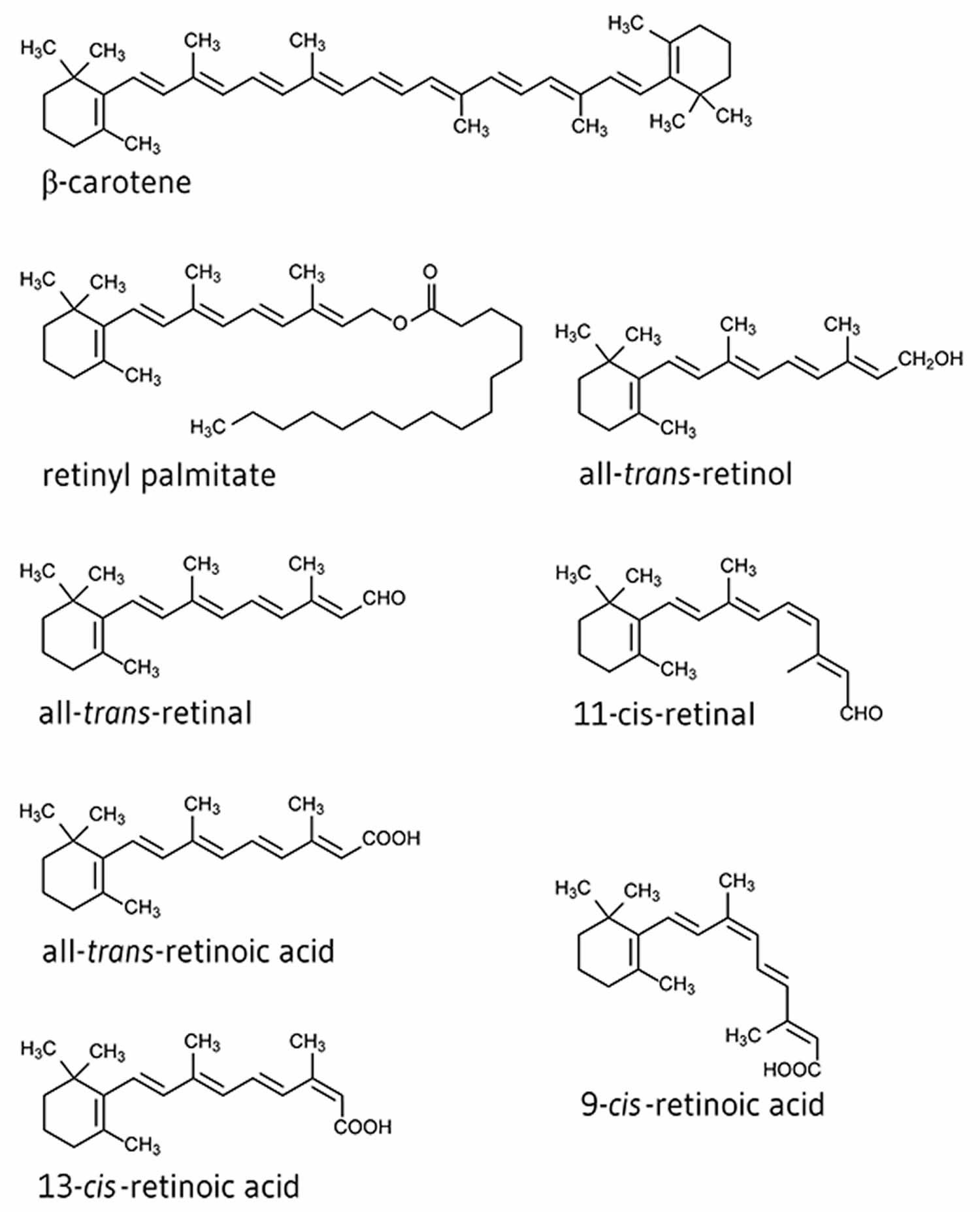
Vitamin A is a general term encompassing various fat-soluble substances such as retinol, retinyl palmitate, and beta-carotene. Its various metabolites are essential for vision, cellular differentiation, epithelial barrier function, and immune function. Vitamin A is obtained through the diet in two forms.

Chemical Formula Of Vitamin B6 With Yellow Pills Stock Photo Download Image Now iStock
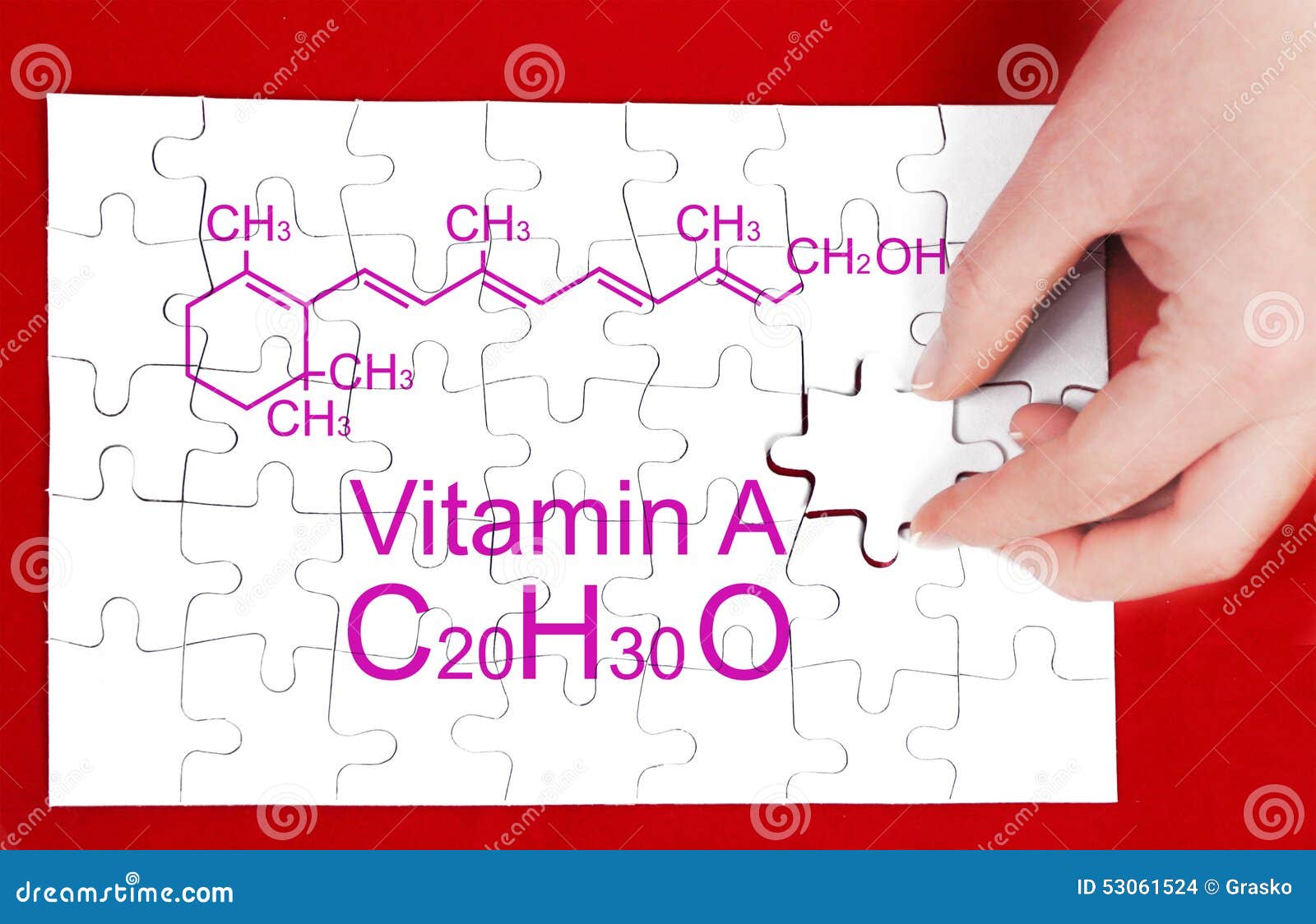
Vitamin A is found in two forms in our diet system- Preformed Vitamin A (found in animal products such as meat, fish, and poultry) and Provitamin A (found in plant-based foods such as fruits and vegetables). (1)(2)(3) Chemical and Physical Features. CAS number: 68-26-8 (2) Molecular Structure: (4) Molecular Formula: C20H30O (2) Weight: 286.45g.

Best Chemical Formula For Vitamin Your Best Life
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin, a category that also includes vitamins D, E and K. The vitamin encompasses several chemically related naturally occurring compounds or metabolites, i.e., vitamers, that all contain a β-ionone ring. [3]
Retinol High Resolution Stock Photography and Images Alamy
Chemical names Chemical Properties Biochemical Functions 1. Visual cycle 2. Other Biochemical Functions Deficiency Disorders Overdose of Vitamin A What are the benefits of vitamin A? Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Vitamin A Which foods are high in vitamin A? What does vitamin A do in the human body? How do we get vitamin A?

Vitamin A, Betacarotene Benefits, Deficiencies, Foods, Interactions
Vitamin A is a general term encompassing various fat-soluble substances such as retinol, retinyl palmitate, and beta-carotene. Its various metabolites are essential for vision, cellular differentiation, epithelial barrier function, and immune function. Vitamin A is obtained through the diet in two forms. Preformed vitamin A (retinol and retinyl.

Vitamin B6 Chemical Structure
The Daily Value used in nutrition labelling is based on 1000 RE of vitamin A for a reference diet (Note: RE equals retinol equivalents). For example, if a food product has 132 RE of vitamin A, the product would have a % Daily Value for vitamin A of 13%. (132 RE ÷ 1000 RE) × 100 = 13%.

Vitamin B7. Biotin Molecular Chemical Formula. Infographics. Vector Illustration On Black
Retinyl acetate ( retinol acetate, vitamin A acetate) is a natural [dubious - discuss] form of vitamin A which is the acetate ester of retinol. It has potential antineoplastic and chemopreventive activities. [2] [3]

Molecular structure of vitamin C Stock Image C040/4336 Science Photo Library
Context 1. A, also called retinol (the active form of vitamin A), is a fat-soluble vitamin with a molecular formula C20H30O and molar mass: 286.45 g/mol. The IUPAC name is 3,7-dimethyl-9-.
/vitamin-a-58b602a35f9b5860464ca3cf.png)
Vitamin Chemical Structures
When the body requires vitamin A, it is released from the liver, transported in the blood by the retinol binding protein, and subsequently delivered to other tissues. Animal Sources: Animal-derived foods are rich in preformed vitamin A. Prime sources include liver, kidney, egg yolk, milk, cheese, and butter.
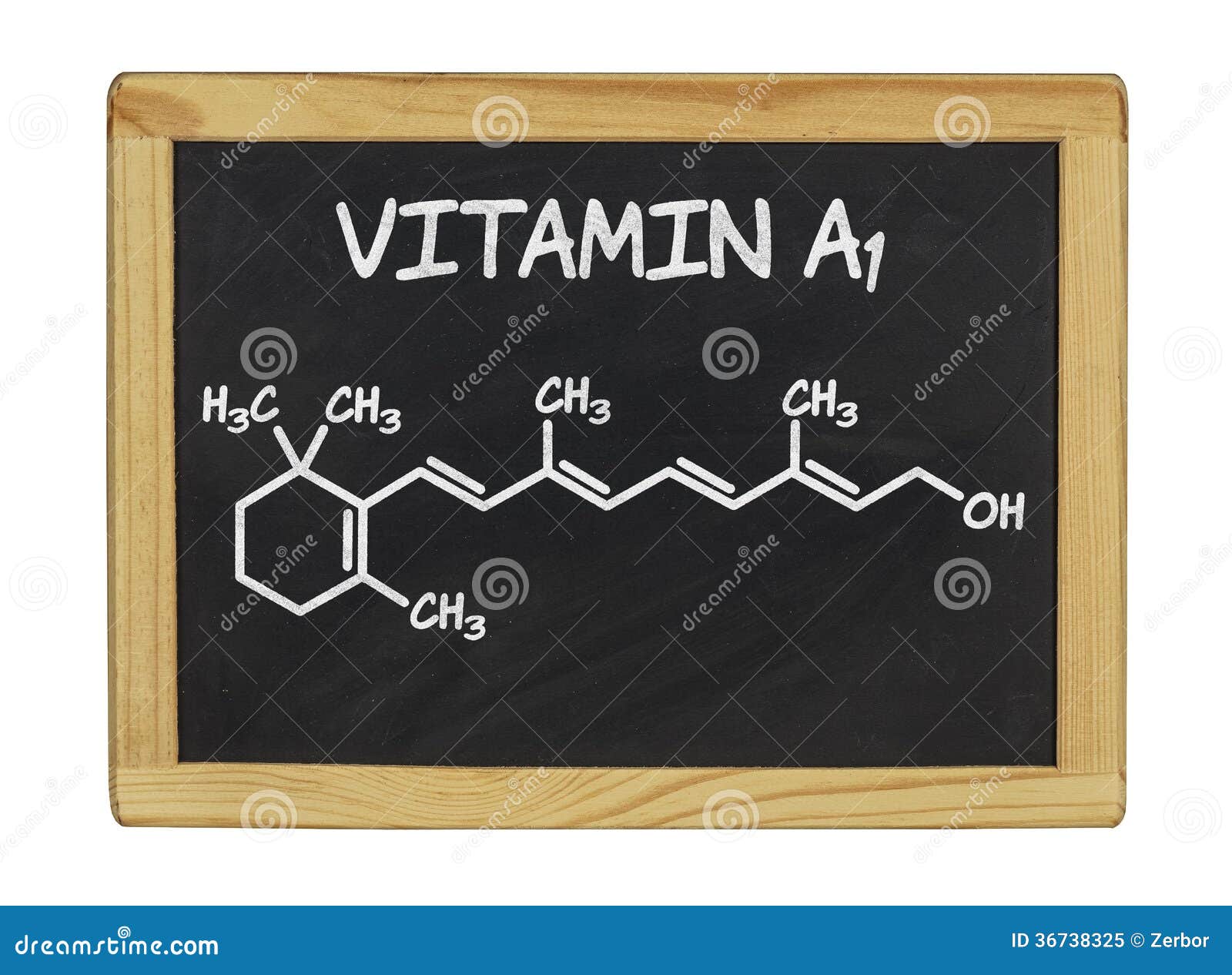
Chemical Formula of Vitamin a Stock Image Image of atom, board 36738325
Publisher Summary. This chapter discusses the chemistry and physiology of vitamin A. Chemical work on vitamin A depends on the establishment of biological activity. In the preparation of vitamin A concentrates by extraction from fish liver oils, the distribution of the vitamin can be adequately checked by determination of the ultraviolet.
Hypervitaminosis A, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment & prognosis
applications), vitamin A palmitate 4 (for application in human nutrition), and retinol 1 itself (applications in personal care, mainly in skin-care products). Retinal 5 and retinoic acid 6 are the oxidized forms of retinol and make up the family of the retinoids. 2023 marks 75 years of chemical production of vitamin A acetate.
Vitamin A Stock Photo Image 53061524
Vitamin A: β-Carotene is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) β-carotene is the molecule that gives carrots, sweet potatoes, squash, and other yellow or orange vegetables their orange color. It is part of a family of chemicals called the.

The chemical structure of different forms of vitamin A. Download Scientific Diagram
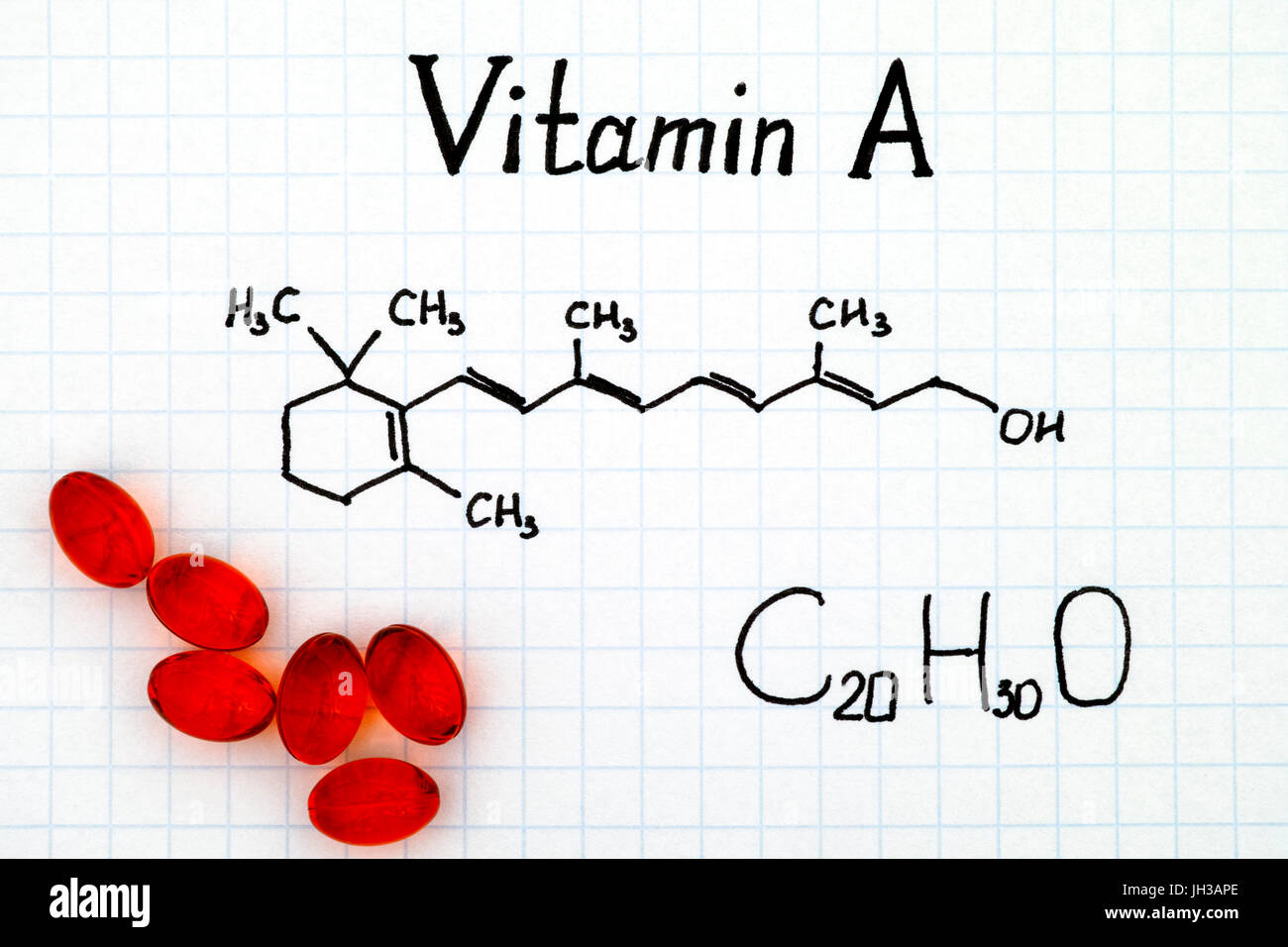
Retinol Retinol, also called vitamin A1, is a fat-soluble vitamin in the vitamin A family that is found in food and used as a dietary supplement. [2] Retinol or other forms of vitamin A are needed for vision, cellular development, maintenance of skin and mucous membranes, immune function and reproductive development. [2]
Vitamin B3 chemical formula. Vitamin B3 structural chemical formula isolated on transparent
1 331 Click to enlarge Vitamins are an important part of our diet, but you probably haven't given a great deal of thought to their chemical structures. This graphic shows chemical structures for all 13 vitamins; though there can be some variability in these structures in sources of the vitamins, these are generally representative.
Vitamin B8 Inositol Molecular Structure. Vitamin B8 Inositol Skeletal Chemical Formula. Chemical
The structure of vitamin A - PMC. Journal List. Biochem J. v.26 (4); 1932. PMC1261021. As a library, NLM provides access to scientific literature. Inclusion in an NLM database does not imply endorsement of, or agreement with, the contents by NLM or the National Institutes of Health.
