
Fetus 4 Months Stock Photo Download Image Now iStock
Fetus in fetu is a rare congenital anomaly that occur secondary to abnormal embryogenesis in a diamniotic monochorionic pregnancy [1]. It was first described in the 1800s by Johann Friederich Meckle [2]. Less than 200 cases of fetus in fetu have been reported till now [3]. It is unusual condition in which a vertebrate fetus is enclosed within.

Foetus Humain Dans Les Womb 40 Semaines De Gestation Photo Getty Images
Fetus in fetu (FIF) is a rare congenital anomaly with an incidence of 1 in 500,000 live births with male predominance. It occurs from anomalous embryogenesis in a diamniotic monochorionic twin pregnancy in which a malformed monozygotic twin lies within the body of fellow twin. The most common location is the retroperitoneum and the other being.

Normal Anatomy of the Fetus at MR Imaging RadioGraphics
Fetus-in-fetu is a rare entity estimated to occur in 1:500,000 deliveries, with fewer than 100 cases reported worldwide [].Generally, fetus in fetu is a single parasitic twin, but there can be multiple fetuses-in-fetu sometimes [].It is predominantly retroperitoneal in 80% of cases, while reported uncommon sites include the oral cavity, sacrococcygeal region, and scrotum [3, 4].

Placenta’s alarm clock signals when it’s time for birth to begin New
Absract: Fetus-in-fetu (FIF) is an extremely rare anomaly of monochorionic diamniotic twins in which a malformed fetus resides in the body of its normal sibling during development.Prenatally, FIF presents as a complex, well circumscribed intrafetal mass which is usually detected during the second or third trimesters at the time of a routine scan.

Normal Anatomy of the Fetus at MR Imaging RadioGraphics
Background: Fetus in fetu is a rare congenital anomaly in which malformed fetus grows within the body of its twin. It is almost always detected as an abdominal mass in infancy. It is a parasitic twin of a diamniotic, monozygotic twin. It should be differentiated from teratoma which has no axial arrangement and has got definite malignant potential.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/fetus--baby--in-womb-anatomy-1064521624-63213b17dfd549f4a418f90aa0f7a91e.jpg)
Placenta Anatomy, Function, and Treatment
Fetus in fetu (FIF) is a rare congenital anomaly with an incidence of 1 in 500,000 live births. It was first described by Meckel, a German anatomist. FIF is a malformed parasitic twin found inside the body of its host co-twin, usually in the abdominal cavity. It is formed as a consequence of an unequal division of the totipotent inner cell mass.

Revisiting fetusinfetu Annals of Saudi Medicine
The growth of a fetus in fetu initially parallels its twin in the uterus, but it abruptly stops because of the vascular dominance of the host twin or an inherent defect in the parasitic twin [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. Fetus in fetu is always anencephalic, but the vertebral column and the limbs are present in almost all cases (91% and 82.5%, respectively).

Fetal development week by week BabyCenter
Fetus in fetu is a rare congenital anomaly and is defined as a monozygotic twin incorporated into the abdomen of its sibling during development. Fetus in fetu is often overlooked in the differential diagnosis of an abdominal mass. Unlike teratomas, fetus in fetu is a benign disorder. We describe the clinical characteristics of two patients, a thirty-months old boy who was found to have.

Normal Anatomy of the Fetus at MR Imaging RadioGraphics
Background: Fetus in fetu (FIF) is a rare entity in which a malformed diamniotic monochorionic parasitic fetal twin develops inside a normal co-twin's body, most commonly in the abdominal cavity. FIF is differentiated from the teratoma by the presence of vertebral column often with an appropriate arrangement of other organs or limbs around it.
Human Fetus At Week 10 Of Gestation Photograph by Sebastian Kaulitzki
Fetus-in-fetu. Imaging and pathology. 2012 Apr;33 (4):444-8. Fetus-in-fetu (FIF), also known as endoparasitic twin, is a form of asymmetric fetal duplication in which the abnormal developing embryo parasitizes the normal co-twin by attaching internally. Here, we report a case of FIF presented as an intra-abdominal cystic mass, which was first.
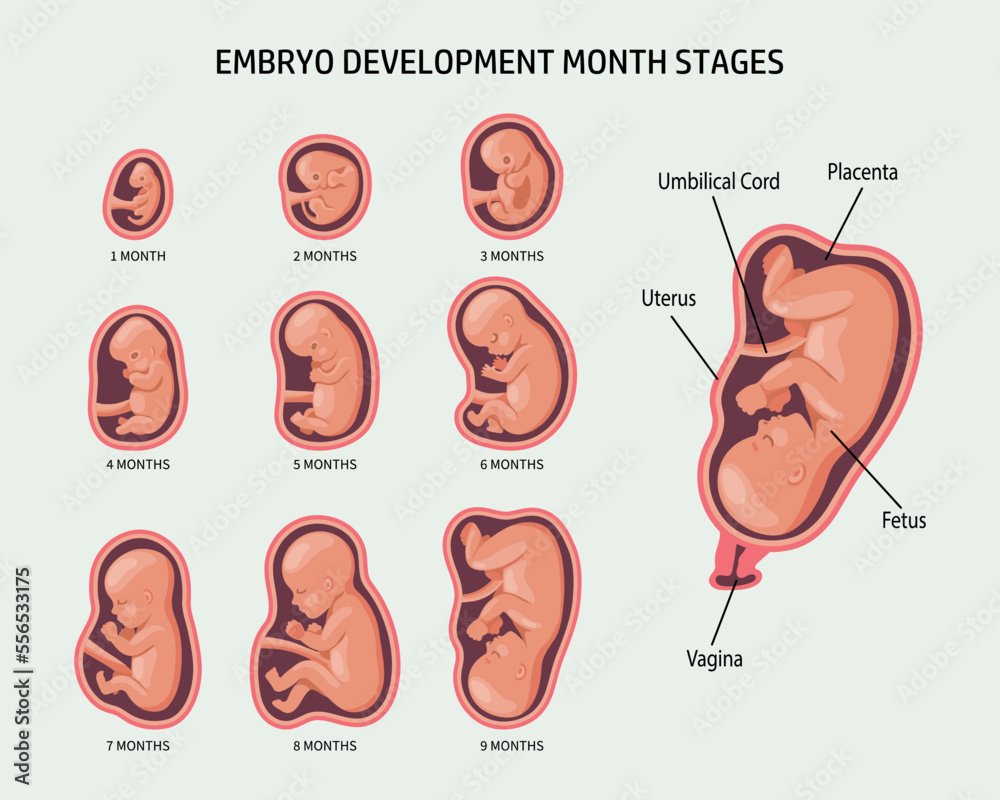
Embryo in the womb, set. Development and growth of the fetus at
Fetus-in-fetu (FIF) is an extremely rare congenital anomaly in which a vertebrate fetus-like mass is situated within the body of its fully developed host. Two main hypotheses on the pathogenesis of FIF have been described. The "included-twin" or "parasitic-twin" theory suggests that FIF arises from an anomalous monozygotic monochorionic.

Fetus Pictures, Images and Stock Photos iStock
Fetus-in-fetu: imaging and pathologic findings Abdom Imaging. 2012 Feb;37(1):147-50. doi: 10.1007/s00261-011-9757-2.. After opening the sac it was noted to contain an incompletely developed fetus with grossly visible limbs, clearly discernible male genitalia, hairs, and a poorly formed head. The fetus was connected to the sac via an 8 cm.

Normal Anatomy of the Fetus at MR Imaging RadioGraphics
1. Background. Fetus in fetu is a rare congenital entity with an incidence of 1 in 500000 births. It is a monozygotic diamniotic twin where the parasitic twin develops inside the body of a host twin [1].Most of the cases are diagnosed before 18 months of age [2].It is found most commonly in the retroperitoneum [3, 4].Atypical locations like skull, sacrum, scrotum and mouth has also been.

Normal Anatomy of the Fetus at MR Imaging RadioGraphics
Introduction "Fetus in fetu" (FIF) is defined as the abnormal monozygotic twin inside the body of its "host twin." Intracranial FIFs are extremely rare. Case presentation A male premature newborn was admitted to the hospital due to a large intracranial tumor diagnosed in the 31st week of gestation. The child died before surgical treatment because of failure of the respiratory system.
Labgrown embryos reveal earliest stages of life Literacy Project
Fetus in fetu is a rare condition which most often presents as a fetiform calcified mass in the abdomen of its host, fetus or newborn. We report a case of 8-month-old girl with history of abdominal distension. Ultrasonography and computed tomography scan revealed a mass in which the contents favor a fetus in fetu rather than a teratoma.

Normal Anatomy of the Fetus at MR Imaging RadioGraphics
Fetus-in-fetu (FIF) is a rare entity in which one malformed vertebrate fetus is enclosed within the body of its twin. This is an extremely rare condition, and Hopkins et al. found less than 100 case reports on extensive review of the literature. An array of presentations is described in the literature although the embryo-pathogenesis and.
