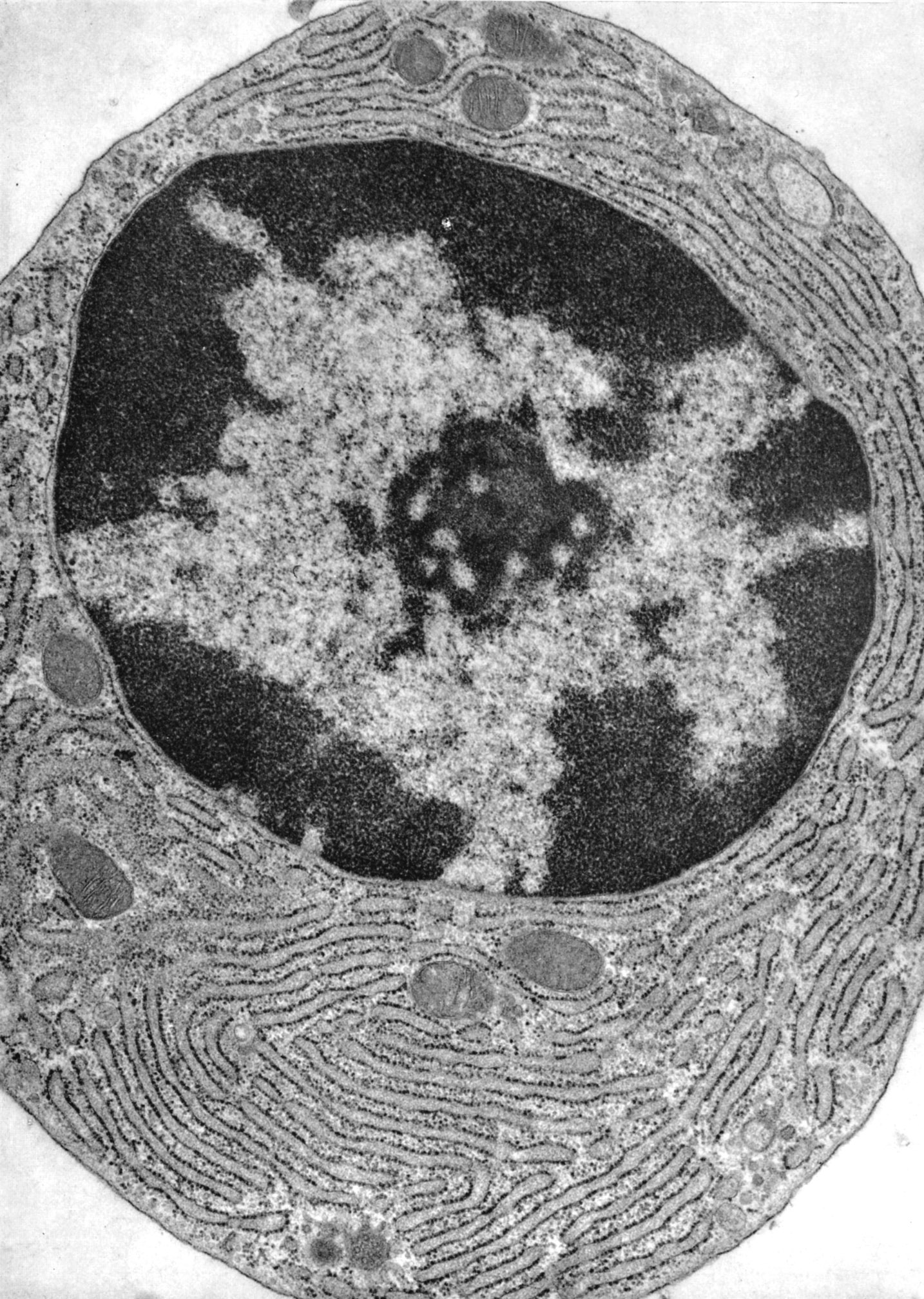
Electron Micrograph
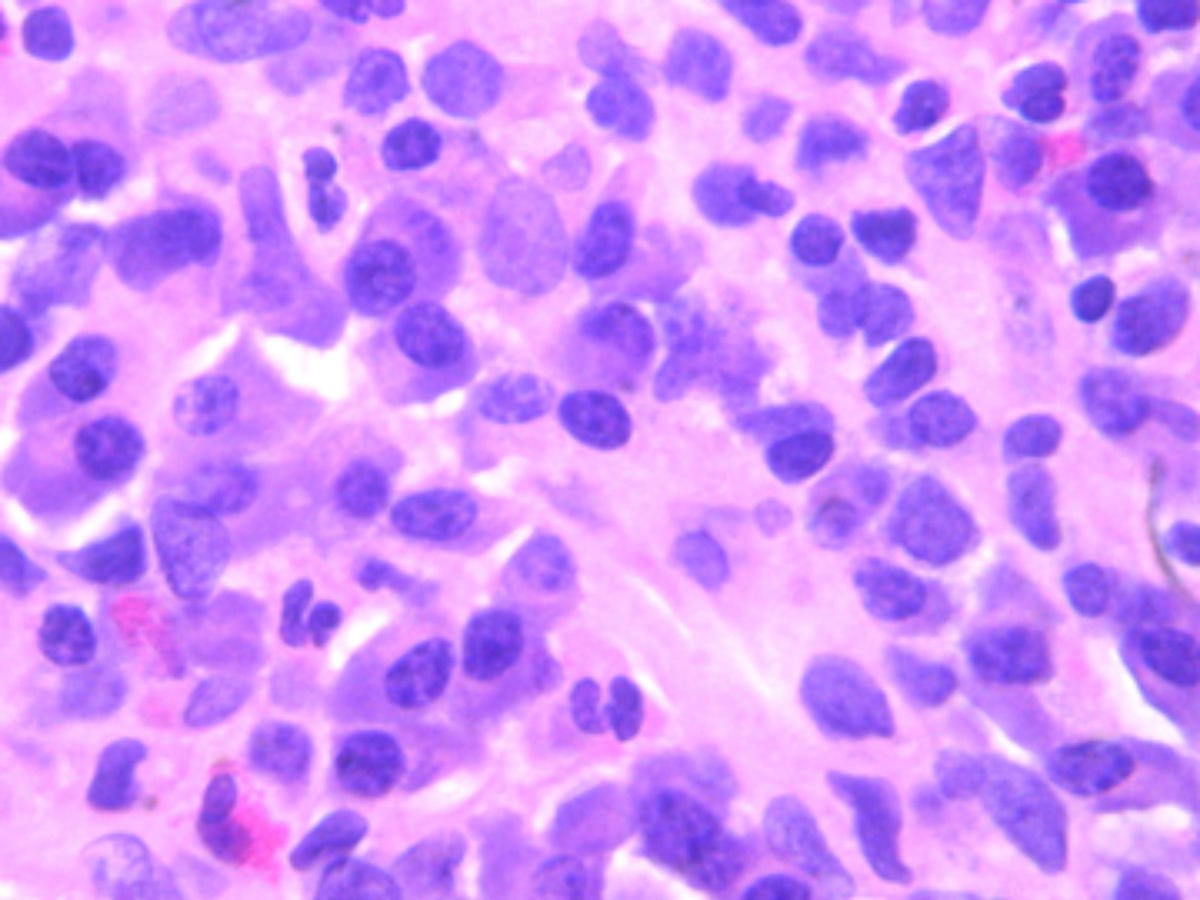
Plasma cells - 1. #00004107. Author: Peter Maslak. Category: Lymphoma: Mature B-cell and Plasma cell Neoplasms > Plasma Cell Neoplasm. Published Date: 11/01/2009. Plasma cells (arrows) have eccentric nuclei characterized by a "clock face" appearance to the chromatin. The cytoplasm may range from basophilic to blue-gray and can contain vacuoles.

Lin’s Lab Unravels the Pathway of Plasma Cells
The first round of anti-CD20 depletion was performed at 1.5 years after vaccination and when tetanus-specific memory B cell frequencies were determined at 1.7 years (2.5 months after depletion.
Plasma cells 1.
Plasma cells are 14 to 20 microns in diameter and are characterized by a strongly basophilic cytoplasm. Electron microscopy reveals an eccentrically-located nucleus that has a well-developed nucleolus and variable amounts of condensed chromatin. Chromatin associated with the nuclear membrane gives the nuclei the appearance of a clock-face or.
An unusual presentation of Castleman's Diseasea case report BMC Infectious Diseases Full Text
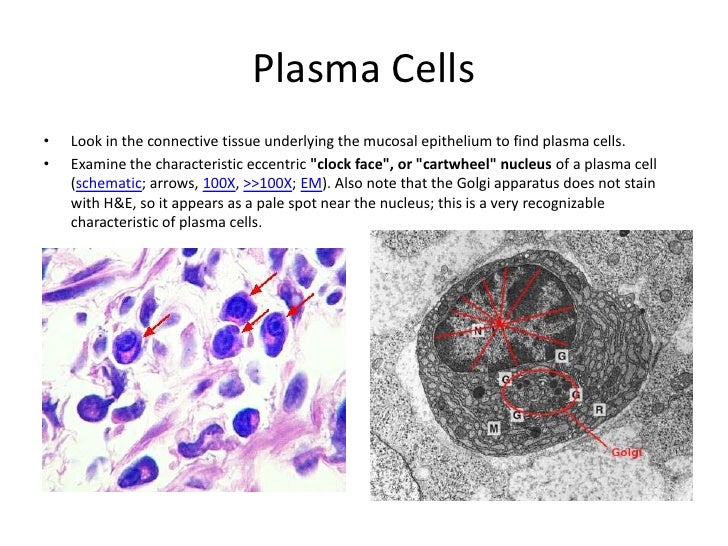
An accumulation of plasma cells demonstrates two diagnostic features that help identify plasma cells. Heterochromatin frequently clumps around the periphery of the nucleus, forming a "clock face" appearance. Additionally, a pale-staining region in the cytoplasm adjacent to the nucleus indicates the position of the large Golgi apparatus.

Figure 14 from Plasma cell morphology in multiple myeloma and related disorders. Semantic Scholar
Plasma cells vary in size from 14 to 20 micrometers. They are round-to-ovoid cells containing abundant deep blue cytoplasm with a pale perinuclear area corresponding to the Golgi apparatus. They have a round, eccentrically placed nucleus with coarse chromatin arranged in a clock face (art wheel) pattern. Most plasma cells are uninucleate; few.

2 Face collection. Plasma Pulse. WatchMaker Watch Faces
B cells: antibody-mediated immunity. Plasma cells: differentiated antibody-producing B lymphocyte. Eccentric nucleus with clock-face chromatin; Now 2/3 of cell is cytoplasm; Russell body: plasma cell that is filled with antibodies and the nucleus has been pushed out. Sign of really chronic inflammation Blood smear with immune cell s. Giant Cells

Multiple Myeloma Stepwards
Plasma cells: Clock face nuclei, paranuclear clearing. Characteristic of chronic inflammation near mucous membranes and often seen around invasive tumours. Lymphocytes and histiocytes: The predominant cell type in most inflammatory skin diseases. Histiocytes are macrophages, and may be seen to have engulfed debris.

Figure 17 from Plasma cell morphology in multiple myeloma and related disorders. Semantic Scholar
The nucleus of the plasma cell is spherical and usually eccentrically positioned. It contains large clumps of peripheral heterochromatin interspersed with clear areas of euchromatin, giving it a characteristic cartwheel or an analog clock face appearance.

Bone Marrow nonneoplastic Plasma cells
Plasma cells have distinctive features that are clearly seen in this electron micrograph: a prominent Golgi; well developed rough endoplasmic reticulum; and a nucleus with large clumps of heterochromatin at the margin of the nucleus (clock-face nucleus). Compare these features with the high magnification light microscopic inset. Plasma cells.
Samantha blum histo study guide 2
Ovoid intermediate-small cell size ~ 12 micrometers: Cells slightly larger than red blood cells and neutrophils. Eccentric nucleus. Nucleus usu. hugs the cell membrane. "Clock-face" chromatin pattern. Small dots symmetrically rim the nuclear membrane - like the numbers on a clock. Abundant cytoplasm. Nucleus-to-cytoplasm ratio ~1:2.

The plasma cell clockface or cartwheel nuclear pattern as seen in 2D... Download Scientific
Download scientific diagram | Plasma cells are identified by their eccentric, clock-face nucleus and pale perinuclear cytoplasmic crescent. Staining by hematoxylin-eosin stain (magnification 400×.

Cell structure Wall Clock by Admin_CP66866535
Mott cells are plasma cells that have spherical inclusions packed in their cytoplasm. The term 'Mott cell' is named after a surgeon, F. W. Mott, who identified these cells in the brains of monkeys with trypanosomiasis (1901). He termed it morular cell (from the Latin morus, mulberry) and recognized these cells to be plasma cells and.

Figure 17 from Plasma cell morphology in multiple myeloma and related disorders. Semantic Scholar
The plasma cell clock-face or cart-wheel nuclear pattern as seen in 2D sections/projections from almost any angle can be explained by the multiradial arrangement of peripherally placed clump units.

Sorting strategy of plasma cells representative flow cytometry plots... Download Scientific
Structure Plasma cells with Dutcher and Russell bodies (H&E stain, 100×, oil). Plasma cells are large lymphocytes with abundant cytoplasm and a characteristic appearance on light microscopy.They have basophilic cytoplasm and an eccentric nucleus with heterochromatin in a characteristic cartwheel or clock face arrangement. Their cytoplasm also contains a pale zone that on electron microscopy.

Plasmablastic lymphoma cells with a plasmacytoid appearence with a... Download Scientific Diagram
Multiple Myeloma is neoplastic proliferation of plasma cells that commonly results in multiple skeletal lesions, hypercalcemia, renal insufficiency, and anemia. Patients typically present at ages > 40 with localized bone pain or a pathologic fracture. Diagnosis is made with a bone marrow biopsy showing monoclonal plasma cells ≥10%.
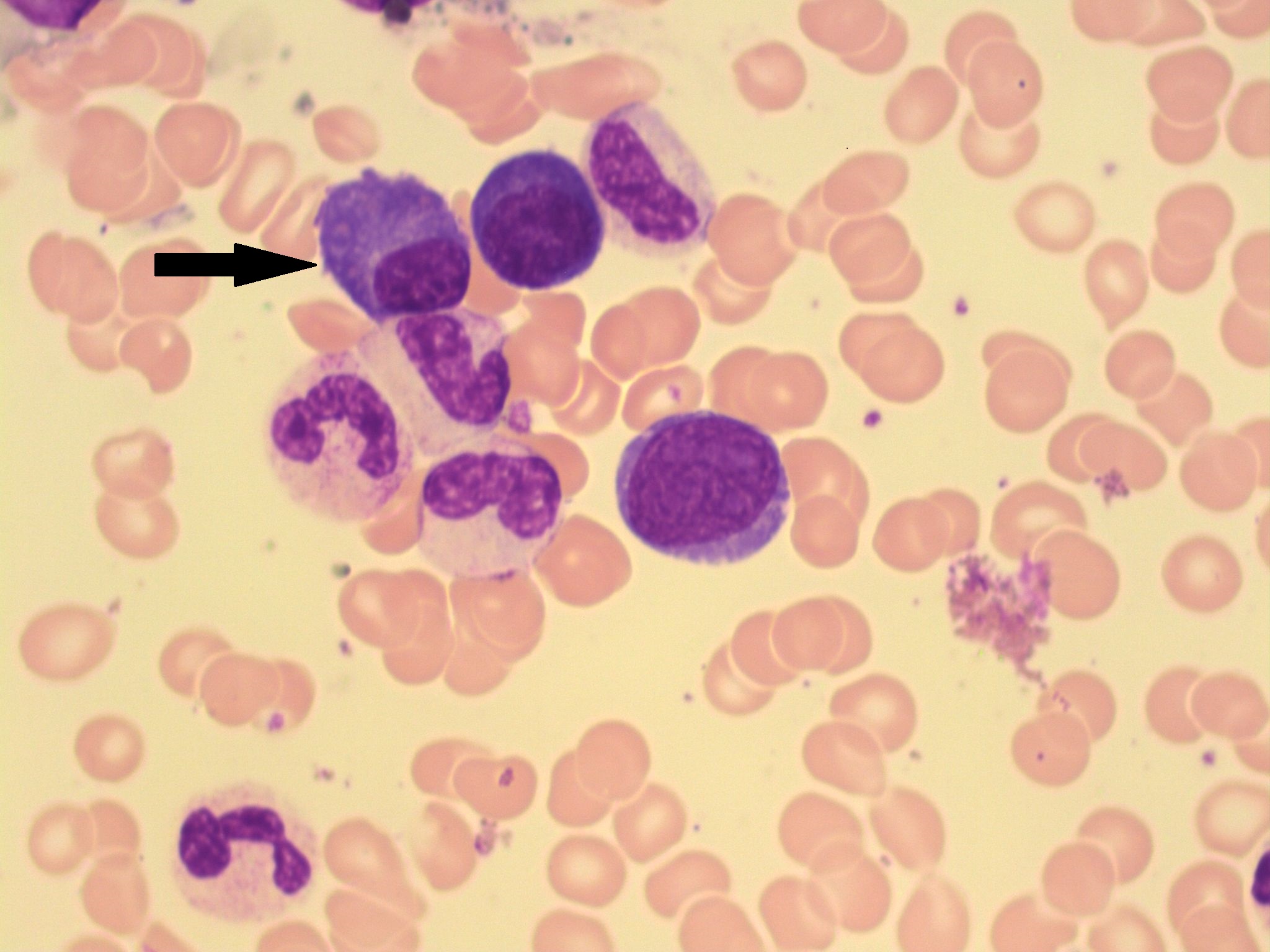
Plasma Cells A Laboratory Guide to Clinical Hematology
Definition / general. Usually less than 1% of marrow cells; rare in infants. Often perivascular and in particle crush specimens. Indeterminate lifespan ranging from days to months. Produces and secretes antibodies. Plasmablast: precursor to plasma cell, produces more antibodies than B cells but less than mature plasma cells.
