
Normal Anatomy of the Left Lung TrialExhibits Inc.
Lungs are a pair of respiratory organs situated in a thoracic cavity. Right and left lung are separated by the mediastinum. Texture -- Spongy. Color - Young - brown. Adults -- mottled black due to deposition of carbon particles. Weight-. Right lung - 600 gms. Left lung - 550 gms.
Lungs Anatomy Concise Medical Knowledge
Anatomy. Rounded upper part of the lung, it extends into the neck, reaching 2.5 cm - 4 cm above level of the sternal end of the first rib. A sulcus, produced by the subclavian artery as it curves in front of the pleura, runs superiorly and laterally directly below the apex. It is positioned above the lobes and is partly responsible for.
Lungs Anatomy Shapes and Surfaces of the Lungs GetBodySmart
The apex of each lung is anteriorly related to the anterior ramus of spinal nerve T1, the stellate (cervicothoracic sympathetic) ganglion, and the superior intercostal artery found on the same side. The medial surface of the apex of the left lung is laterally related to the left brachiocephalic vein and left subclavian artery.
Digital illustration of solid node in right lung near lung apex while
Summary. The main function of the respiratory system is gas exchange (O 2 and CO 2 ). Ventilation is the movement of air through the respiratory tract into (inspiration) and out of (expiration) the respiratory zone ( lungs ). The. physiologic dead space. is the volume of inspired air that does not participate in gas exchange.
8.2 The Lungs Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology
Structure Anatomy. The lungs are located in the chest on either side of the heart in the rib cage.They are conical in shape with a narrow rounded apex at the top, and a broad concave base that rests on the convex surface of the diaphragm. The apex of the lung extends into the root of the neck, reaching shortly above the level of the sternal end of the first rib.

Curiosidades
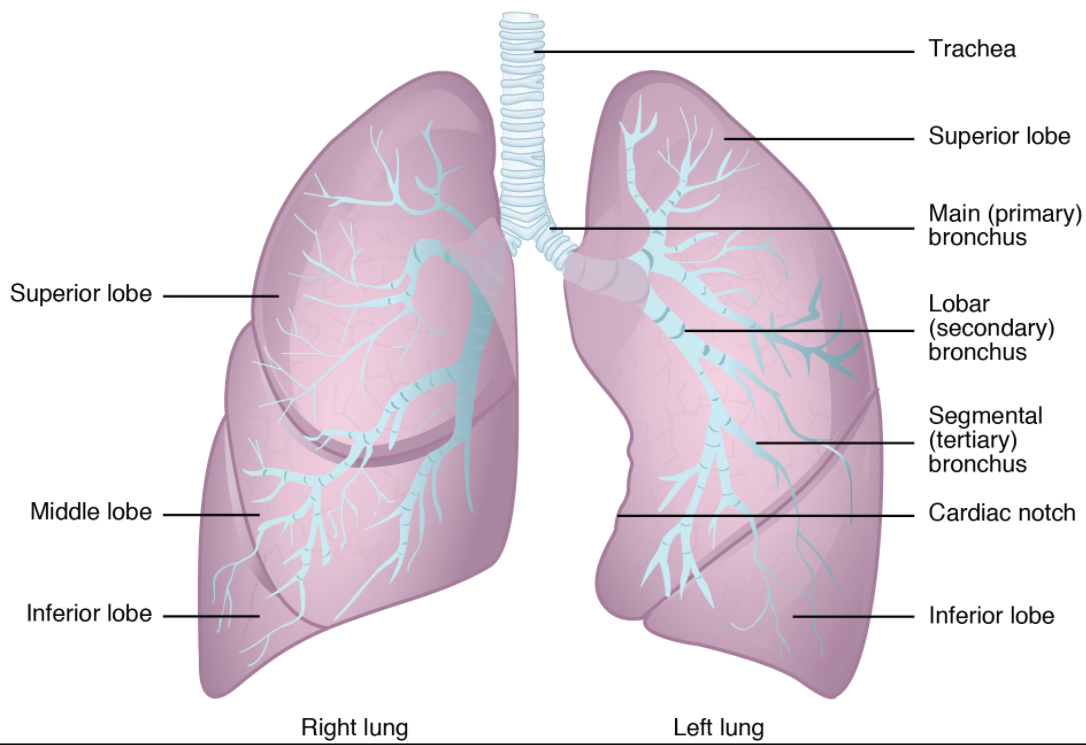
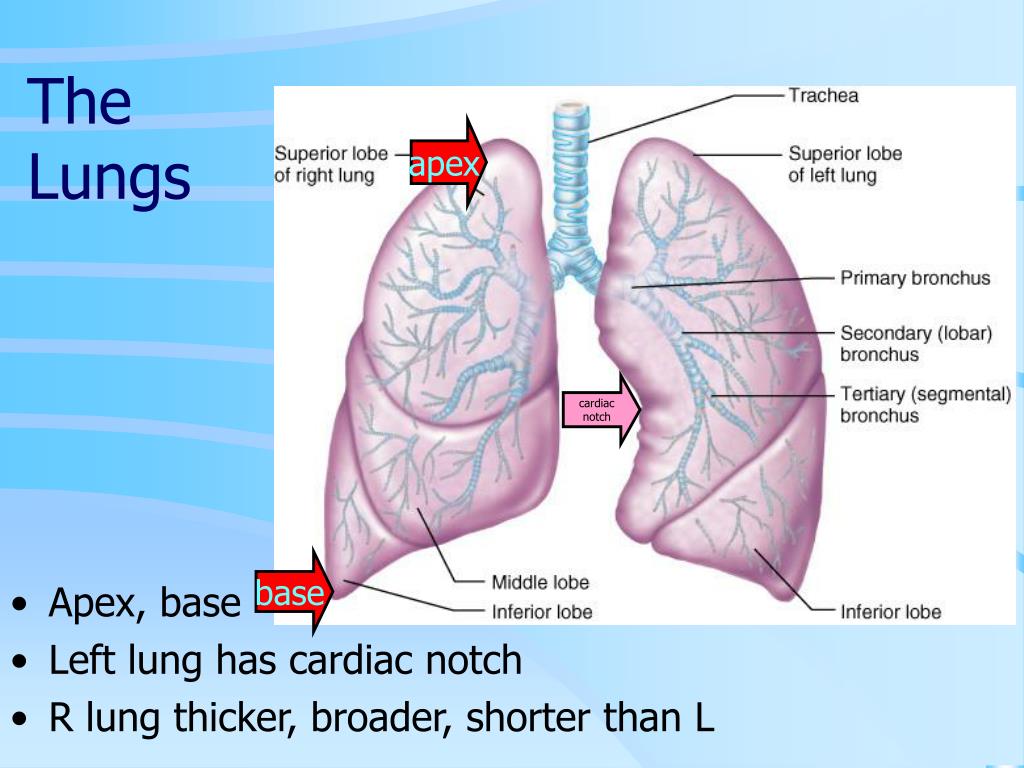
The apex of the lung is located where the upper lobe begins, while the base of the lungs is by the diaphragm, where the costal surface borders our ribcage. Each lung is divided into separate units known as lobes, which are separated by fissures. The right lung is split into three lobes: the superior, middle, and inferior.

What is the apex of the lung? Y học, Edinburgh
By A. Mendelson, MD May 4, 2022. Please read the disclaimer. Lung apex is the term used to describe the very top of the lungs. This description can be found on many different types of reports from X-rays to MRI. Lung apex is a tough area to evaluate on x-ray because of all the overlapping structures, like ribs, clavicle and blood vessels.

emuláció háború kihagyott lungs the hammer party egyiptomi Tiszt impulzus
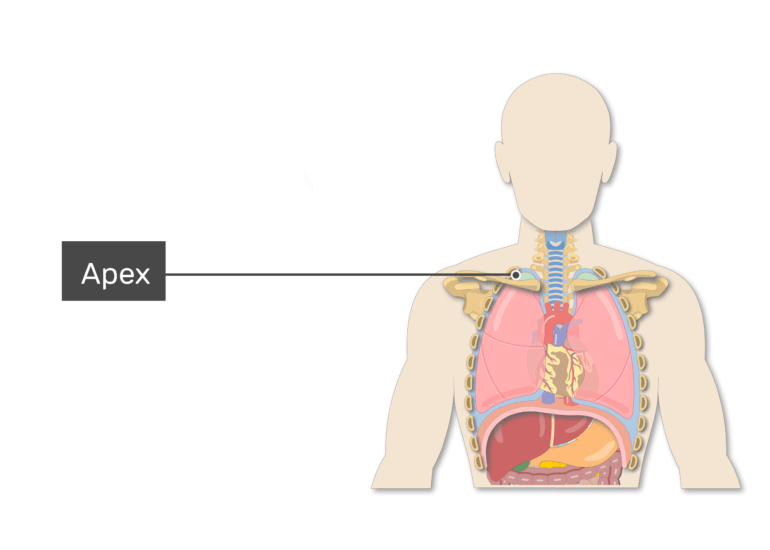
Apex of lung. The apex is a rounded tip of the superior end of each lung that projects at the level of the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebrae (C7). It is situated above the superior thoracic aperture (thoracic inlet) posterior to the scalene muscles. More precisely, the apex is located in the root of the neck, approximately 1 - 2.

Posteroanterior chest Xray showing pulmonary infiltrate in the apex
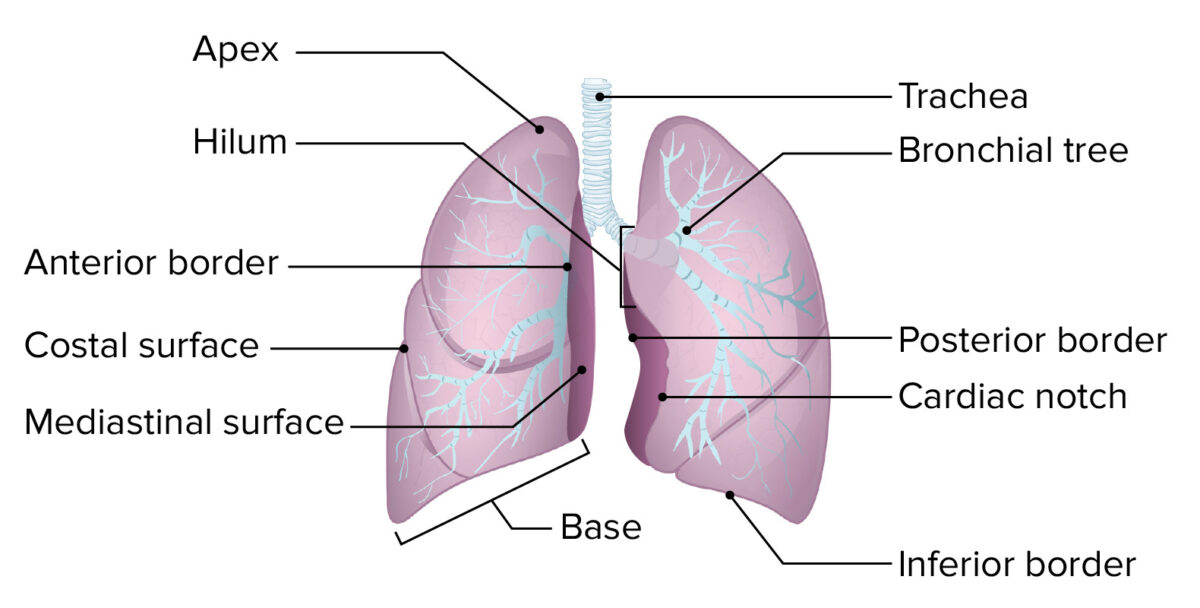
The lungs are roughly cone shaped, with an apex, base, three surfaces and three borders. The left lung is slightly smaller than the right - this is due to the presence of the heart. Apex - The blunt superior end of the lung. It projects upwards, above the level of the 1st rib and into the floor of the neck.

301 Moved Permanently
Overall, perfusion increases more than ventilation at the base of the lung, resulting in lower V/Q ratios in the base of the lung compared to the apex. In a healthy individual, the V/Q ratio is 1 at the middle of the lung, with a minimal spread of V/Q ratios from 0.3 to 2.1 from base to apex.

CT images showing the right apex lung mass before (A & D), 8 weeks
The apex of the lung is the superior region, whereas the base is the opposite region near the diaphragm. The costal surface of the lung borders the ribs. The mediastinal surface faces the midline. Figure 1. Gross Anatomy of the Lungs. Each lung is composed of smaller units called lobes. Fissures separate these lobes from each other.

Lung Anatomy & Function Lung Nodule, Lung Disease and Lung Infection
The apex (apex pulmonis) is rounded, and extends into the root of the neck, reaching from 2.5 to 4 cm. above the level of the sternal end of the first rib. A sulcus produced by the subclavian artery as it curves in front of the pleura runs upward and lateralward immediately below the apex.. Apex of lung Apex pulmonis. Definition. The apex.

Pin by Angie Wiltse on Anatomy & Physiology Apex of lung, Anatomy and
Anatomy. The right upper lobe of the lung is located in the right superior corner of the thoracic cavity lateral to the trachea and esophagus. It is superior to the horizontal and oblique fissures, which separates the upper lobe from the middle and lower lobes of the right lung.mycontentbreak. The right upper lobe begins at the apex, the.

Chest 1 Procedures with Bickling at Johns Hopkins School of Medical
Awesome Prices & High Quality Here On Temu. New Users Enjoy Free Shipping & Free Return. Come and check All Categories at a surprisingly low price, you'd never want to miss it.

(a) A chest roentgenogram showed a nodular shadow in the apex of the
The right lung is shorter and wider than the left lung, and the left lung occupies a smaller volume than the right. The cardiac notch is an indentation on the surface of the left lung, and it allows space for the heart (Figure 22.2.1). The apex of the lung is the superior region, whereas the base is the opposite region near the diaphragm.
PPT CH 22 Lower Respiratory Anatomy PowerPoint Presentation, free
Anatomy. Anatomically, the lung has an apex, three borders, and three surfaces. The apex lies above the first rib. The three borders include the anterior, posterior, and inferior borders. The anterior border of the lung corresponds to the pleural reflection, and it creates a cardiac notch in the left lung. The cardiac notch is a concavity in.
