
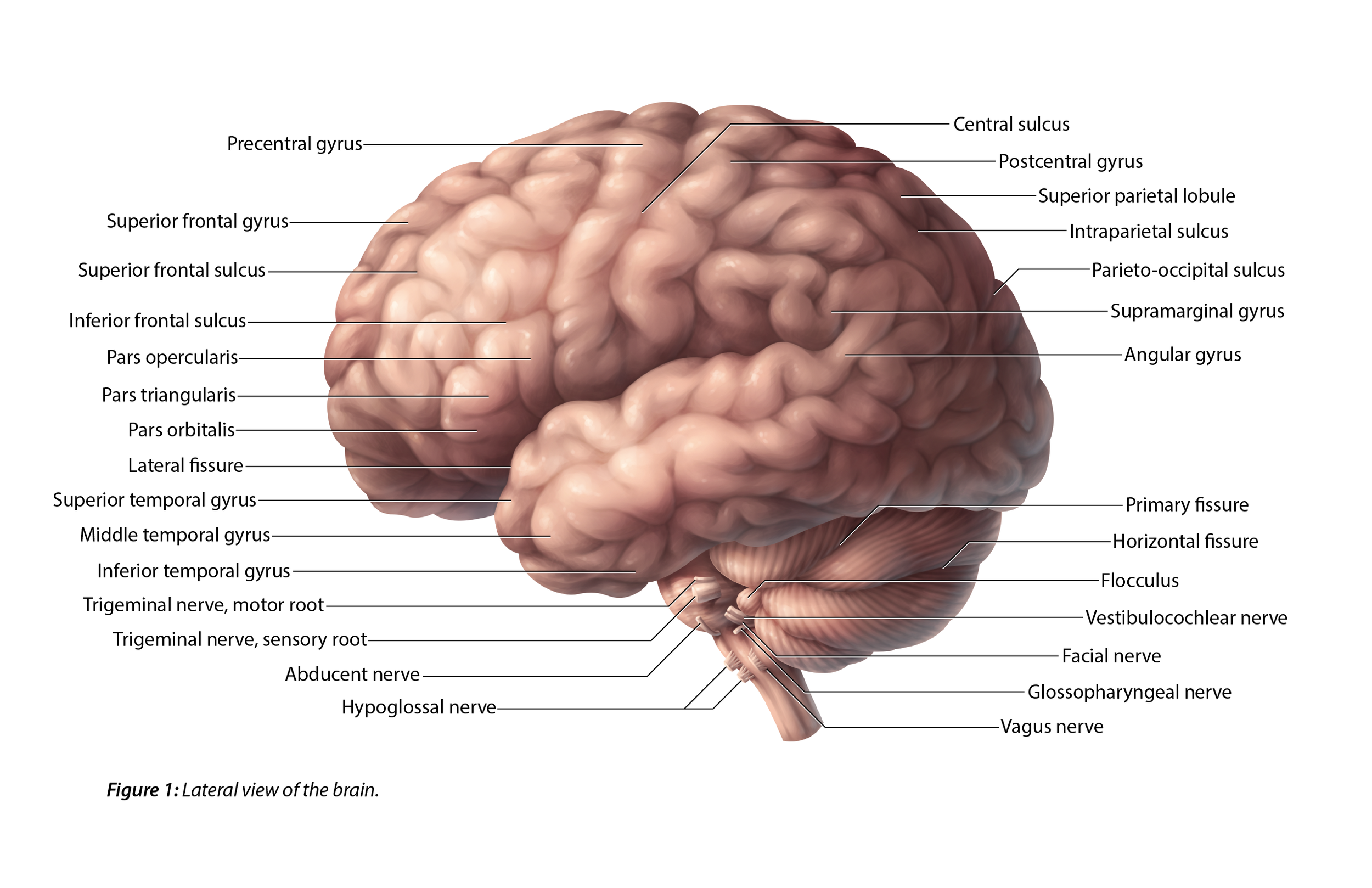
Lateral view of the cerebral cortex showing the principal gyri and
Lobes of brain as well as ventricles: left lateral view. 2. Axial view of brain normal anatomy. 1. Premotor, supplementary motor and primary cortex: left lateral view of brain. 3. . Premotor, supplementary motor and primary cortex: medial view of brain. 1. Highlighted brain structures: axial view.

Brain, Lateral View, Illustration Stock Image F031/8202 Science
Now, view the lateral surface of either hemisphere near the lateral terminus of the central sulcus (see Figure 1.9).On the inferior-lateral aspect of the hemisphere, you should readily appreciate a deep and fairly straight fissure that separates the frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobe; this space is called the lateral fissure or Sylvian fissure (named after the important.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/358/uLfuLJ9rHRck46lIV8CvA_lateral-views-of-the-brain_english.jpg)
Lateral view of the brain Anatomy and functions Kenhub
The tissue that connects the two cerebral hemisphere allowing communication between the left and right sides of the brain. Contains the visual center of the brain. (Visual processing/perception) Responsible for the regulation and coordination of complex voluntary muscular movement and maintenance of posture and balance.
Lateral and Sagittal Views of the Brain — B Cheung Biomedical
The brain's cerebral cortex is the outermost layer that gives the brain its characteristic wrinkly appearance. The cerebral cortex is divided lengthways into two cerebral hemispheres connected by the corpus callosum. Traditionally, each of the hemispheres has been divided into four lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital . Although.
Lateral Brain Anatomy
SURFACE ANATOMY OF THE BRAIN THE LATERALSURFACE OFTHE BRAIN /o) Cross Feotures (b) SelectedGyri,Sulci, ond Fissures (c) CerebrolLobes ond the Insulo (d) Mojor Sensory,Motor, ond Associotion Areos THE MEDIALSURFACE OF THE BRAIN (o) Broin Stem Structures (b) ForebroinStructures (c) Ventricles

the structure of the human brain and its major functions, including the
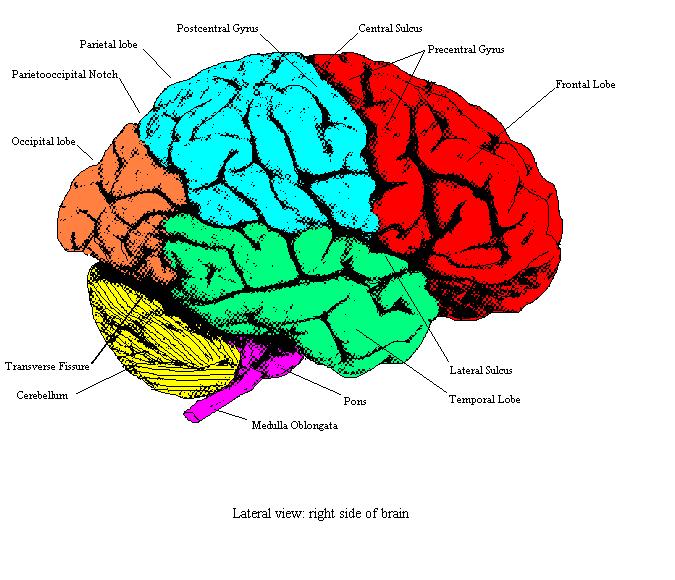
The lateral view of the brain shows the three major parts of the brain: cerebrum, cerebellum and brainstem . A lateral view of the cerebrum is the best perspective to appreciate the lobes of the hemispheres. Each hemisphere is conventionally divided into six lobes, but only four of them are visible from this lateral perspective.
New York: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone. Fig 22.1: Lateral aspect of the left cerebral hemisphere indicating the major gyri and sulci, Fig. 22.2: Sagittal section of the brain, with the brain stem removed, showing the medial aspect of the left cerebral hemisphere, Fig. 22.3: Left lateral aspect of the brain, and Fig: 22.4: The medial surface.

Pin on Brain
cerebral angiogram (DSA): lateral cerebral angiogram (DSA): frontal Head and neck CT head: bone window axial skull base CT head: bone window axial calvarium CT facial bones/orbits: axial

Lob some Lobes in the Ultimate Brain Battle!
Topography of the cerebral hemispheres. Structures seen on the lateral view of the brain. The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, spanning all three cranial fossae. The composite parts can be classified based on their embryological origin, functional roles or their topography. This article will be looking at the organization of the brain.

pars opercularis Google Search Medical school quotes, Brain mapping
The other groove worth noting is the lateral fissure. This one runs roughly along the anterior-to-posterior direction, and curves gently dorsally. Again, in a sagittal view, it is roughly seen in the middle third of the brain in the anterior-posterior axis. Figure 23.1 An external side view of the parts of the brain.
Drawing Of The Brain With Labels at GetDrawings Free download
Building a Digital Brain (Fingers to Gyri) Surface Anatomy of the Brainstem; Blood Supply to the Brain; Lab 2 Overview. you should now be able to view the lateral surface of any hemisphere and know to look for the central sulcus lazily coursing from the longitudinal fissure over the dorsal-lateral surface of the cerebrum in a lateral-ventral.

Chapter 16. Brain The Big Picture Gross Anatomy AccessMedicine
Above: A human brain, lateral view of the left side. The brain is a complex organ with integrated parts. It contains over 100 billion neurons that are specialized to form different regions of the brain. As the brain develops, its neurons develop in complexity, become specialized into specific brain areas and functions, create circuits or.

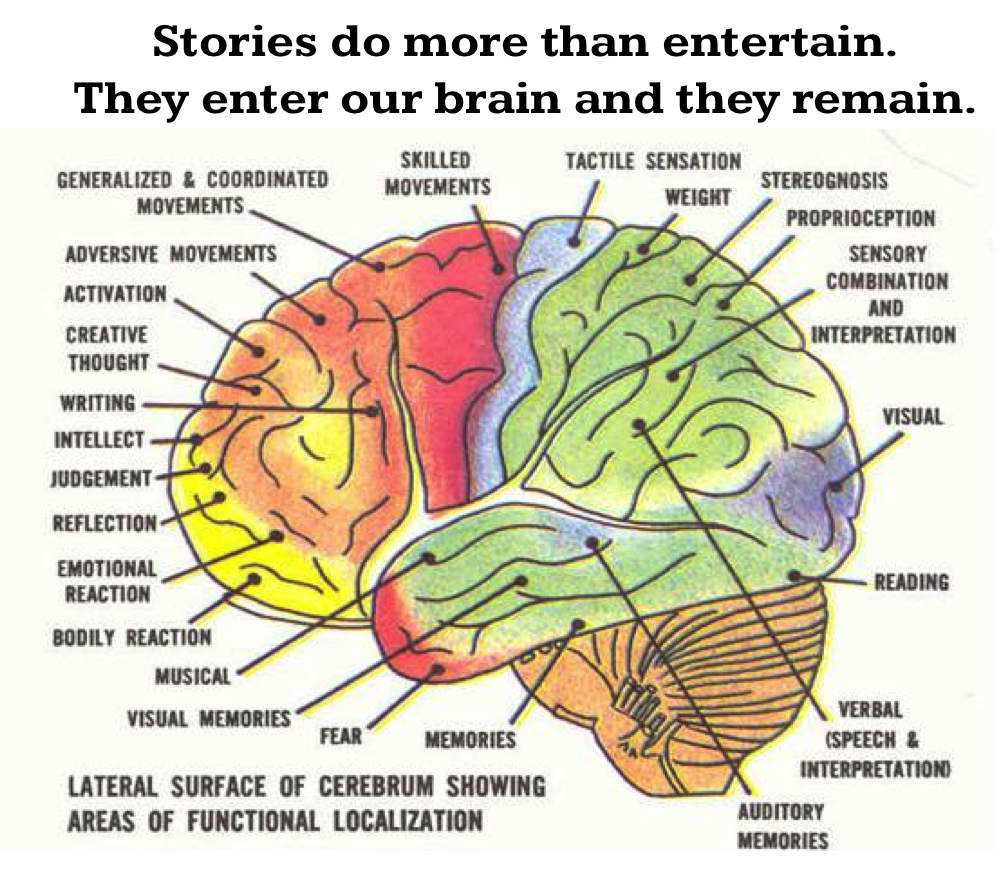
Diagram of the lateral view of the human brain, showing the functional
This article describes the anatomy of three parts of the brain (cerebrum, brainstem & cerebellum) seen from a lateral view. Learn this topic now at Kenhub. Connection lost. Please refresh the page. ventricular system and subarachnoid space Blood supply of the brain Spinal cord Pathways of the nervous system Cranial nerves Peripheral nervous.

Lateral Human Brain 4th Neuro Drawing
Lateral ventricle Caudate nucleus Parietal lobe Level of the insula Caudate nucleus Internal capsule Insular lobe Fornix Corpus callosum Level of the corpora quadrigemina Cisterns Optic chiasm Hypothalamus and mammillary bodies Temporal lobes Cerebral peduncles Superior colliculi Occipital lobes and lateral ventricles Highlights Sources + Show all

Draw neat labelled diagram of lateral view of human brain Brainly.in
The hemispheres have many of the same functions, for example, each perceives touch on one side of the body, but some functions, like language, demonstrate laterality, meaning they are primarily controlled on one side of the brain. The cerebral hemispheres in humans have many folds to increase the surface area of the brain.

Pin on Anatomy and physiology 1
Meninges. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless liquid that bathes the external surfaces of the brain. It is constantly produced, flows through the network of ventricles, and is reabsorbed.
